Overwhelming evidence for the global climate and oceans
disruption Earth emergency (updated Dec 2019)
disruption Earth emergency (updated Dec 2019)
MORE ON THE EMERGENCY
o It is common knowledge there has been no substantive progress towards a new UN international agreement to control global greenhouse gas emissions with the latest 2012 Bonn talks ending in discord and disappointment.
o Atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are extreme record highs compared to their 800,000 maximum, which is 300 ppm for CO2 and 790 ppb for methane (IPCC 2007) For current atmospheric gas levels see www.stateofclimate.com
o Global greenhouse gas emissions are at a record and are still increasing which is on a heading for a catastrophic 6° C temperature increase by 2100 (IEA May 2012)
o CO2 is being added to the atmosphere at 14,000 times faster than natural processes can remove it (Nature Geoscience 2008) making atmospheric CO2 increase at an unprecedented rate (IPCC 2007).
o All atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are maintaining and increasing trajectory (NOAA 2011).
o All world energy and economic plans are for continued dependency on fossil fuels and increasing combustion of fossil fuels with world energy consumption doubling between 1990 and 2035 with 80% from fossil fuels (IEA 2012).
o An immediate global rapid drastic reduction in emissions would still lead to a global warming of over 3°C due to climate system science committed global temperature increase.
o Climate experts think the world is likely now committed to 4° C (Climate change scientists warn of 4° C global temperature rise 2010), (Prof K Anderson and A Bows).
o Because of the climate system inertia and momentum any temperature increase this century will almost double after centuries 2100 (NRC 2010).
o Global warming lasts more than 1000 years (S Solomon PNAS 2010).
At above 1° C billions of people lose availability of water and food and suffer increasing health impacts (IPCC 2007).
o Arctic summer sea ice is collapsing (PIOMAS ice volume record) (Prof C Duarte 2012) with 2012 a record low extent by a wide margin. This is a planetary emergency.
o The Arctic summer sea ice is in a meltdown situation and on a trend resulting in an ice free Arctic in a matter of years rather than decades according to extrapolation of current trend, (When will the summer arctic be nearly sea ice free? J E. Overland 2013, Prof Peter Wadhams (UK) public statements and W. Maslowski (US) - in as early as a few years.
The loss of Arctic snow and sea ice albedo cooling impacts the weather and changes the climate of the Northern hemisphere (J Francis et al .) (J Francis 2012 Evidence linking Arctic amplification to extreme weather in mid-latitudes)
o All sources of Arctic methane feedback emissions are operant (Arctic Feedbacks Global Implications WWF.
o Arctic sub sea methane hydrate destabilizing ( Warming Of Arctic Current Over 30 Years Triggers Release Of Methane Gas) (Methane Releases from Arctic Shelf May Be Much Larger and Faster Than Anticipated 2010).
o Climate-changing methane 'rapidly destabilizing' off US East Coast, study finds October 2012
o Renewed increase in atmospheric methane due to planetary feedback emissions (E. J. Dlugokencky 2009) (NOAA 2011). Arctic methane is above 1900 ppb while the maximum atmospheric methane over the past 800,000 years is 800 ppm by the ice core data.
o Increasing severe weather events. Extreme Weather of Last Decade Part of Larger Pattern Linked to Global Warming Nature Mar 2012
o Ocean acidification is at an unprecedented rate in past 300 million years.
The Geological Record of Ocean Acidification. Science, March 2, 2012
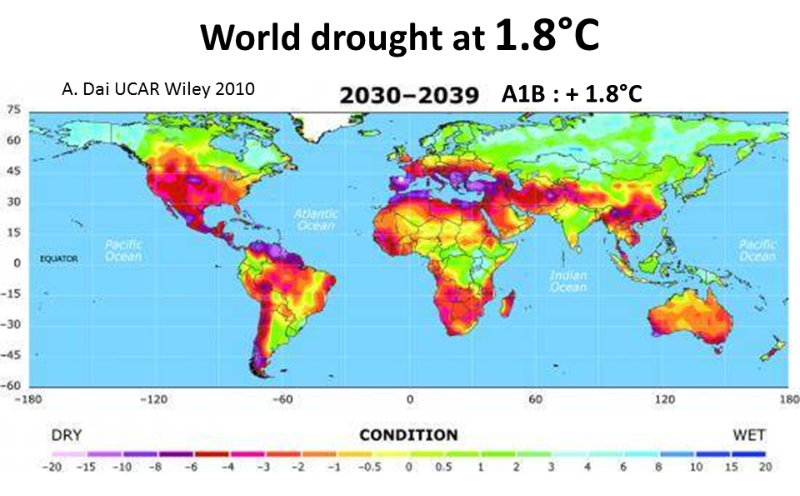
o Increasing global drought (Burke et al Hadley 2006), will increase further as Drought threatens most of the world(Dai 2010). Loss of Arctic snow and ice albedo cooling will increase and prolong the above drought even more.
o The abstracts of the oral and poster presentations to the Arctic Ocean Acidification Conference,at Bergden, Norway, in May of 2013 may be read here. The conference was organized by the Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP), the Institute of Marine Research (IMR), the Norwegian Institute for Water Research (NIVA), the Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research (SCOR), and the University of British Columbia (UBC).
o It is common knowledge there has been no substantive progress towards a new UN international agreement to control global greenhouse gas emissions with the latest 2012 Bonn talks ending in discord and disappointment.
o Atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are extreme record highs compared to their 800,000 maximum, which is 300 ppm for CO2 and 790 ppb for methane (IPCC 2007) For current atmospheric gas levels see www.stateofclimate.com
o Global greenhouse gas emissions are at a record and are still increasing which is on a heading for a catastrophic 6° C temperature increase by 2100 (IEA May 2012)
o CO2 is being added to the atmosphere at 14,000 times faster than natural processes can remove it (Nature Geoscience 2008) making atmospheric CO2 increase at an unprecedented rate (IPCC 2007).
o All atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are maintaining and increasing trajectory (NOAA 2011).
o All world energy and economic plans are for continued dependency on fossil fuels and increasing combustion of fossil fuels with world energy consumption doubling between 1990 and 2035 with 80% from fossil fuels (IEA 2012).
o An immediate global rapid drastic reduction in emissions would still lead to a global warming of over 3°C due to climate system science committed global temperature increase.
o Climate experts think the world is likely now committed to 4° C (Climate change scientists warn of 4° C global temperature rise 2010), (Prof K Anderson and A Bows).
o Because of the climate system inertia and momentum any temperature increase this century will almost double after centuries 2100 (NRC 2010).
o Global warming lasts more than 1000 years (S Solomon PNAS 2010).
At above 1° C billions of people lose availability of water and food and suffer increasing health impacts (IPCC 2007).
o Arctic summer sea ice is collapsing (PIOMAS ice volume record) (Prof C Duarte 2012) with 2012 a record low extent by a wide margin. This is a planetary emergency.
o The Arctic summer sea ice is in a meltdown situation and on a trend resulting in an ice free Arctic in a matter of years rather than decades according to extrapolation of current trend, (When will the summer arctic be nearly sea ice free? J E. Overland 2013, Prof Peter Wadhams (UK) public statements and W. Maslowski (US) - in as early as a few years.
The loss of Arctic snow and sea ice albedo cooling impacts the weather and changes the climate of the Northern hemisphere (J Francis et al .) (J Francis 2012 Evidence linking Arctic amplification to extreme weather in mid-latitudes)
o All sources of Arctic methane feedback emissions are operant (Arctic Feedbacks Global Implications WWF.
o Arctic sub sea methane hydrate destabilizing ( Warming Of Arctic Current Over 30 Years Triggers Release Of Methane Gas) (Methane Releases from Arctic Shelf May Be Much Larger and Faster Than Anticipated 2010).
o Climate-changing methane 'rapidly destabilizing' off US East Coast, study finds October 2012
o Renewed increase in atmospheric methane due to planetary feedback emissions (E. J. Dlugokencky 2009) (NOAA 2011). Arctic methane is above 1900 ppb while the maximum atmospheric methane over the past 800,000 years is 800 ppm by the ice core data.
o Increasing severe weather events. Extreme Weather of Last Decade Part of Larger Pattern Linked to Global Warming Nature Mar 2012
o Ocean acidification is at an unprecedented rate in past 300 million years.
The Geological Record of Ocean Acidification. Science, March 2, 2012
o Increasing global drought (Burke et al Hadley 2006), will increase further as Drought threatens most of the world(Dai 2010). Loss of Arctic snow and ice albedo cooling will increase and prolong the above drought even more.
o The abstracts of the oral and poster presentations to the Arctic Ocean Acidification Conference,at Bergden, Norway, in May of 2013 may be read here. The conference was organized by the Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP), the Institute of Marine Research (IMR), the Norwegian Institute for Water Research (NIVA), the Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research (SCOR), and the University of British Columbia (UBC).
The definite effects of GHG pollution according the basic science
- Combined cumulative effect of:
- global warming
- amplifying climate feedbacks
- climate change and variation
- heat wave increase
- drought increase
- severe storm increase
- flood increase
- chaotic extreme weather event increase
- tropospheric (ground level) ozone increase (toxic to human health and to green plants-crops)
- ocean acidification (and warming)
Today's situation with respect to the science (2016)
- Global warming (and all the above) lasts 1000s of years
- Record global warming 2014, 2015 (NOAa)
- Global surface warming is at least 10X faster than past 65 million years (NRC 2013 Abrupt Climate Chage)
- No simultaneous warming of Northern and Southern hemispheres for 20,000 years
- Committed (locked in) future warming is 2C (IPCC AR5 WG1 12.5.4.2) (today's increase is (0.85C)
- For every incremental increase in emissions there is an added global warming practically irreversible commitment (K Caldiera 2007).
- All crops in all regions will have declined below today's productivity at 2C (or probably less) NRC 2010.
- Global and regional N hemisphere extreme heat events and drought are increasing. Research has found that the increase in global extreme heat has increased 5X (Potsdam) and NH extreme heat (J Hansen New climate dice) are driven by global warming.
- Increasing extreme weather events are a new large source of terrestrial carbon feedbacks (Climate Extremes and the Carbon Cycle Nature Aug 2013). Terrestrial ecosystems absorb approximately 11 billion tons less carbon dioxide every year as the result of the extreme climate events than they could if the events did not occur. That is equivalent to approximately a third of global CO2 emissions per year.
- The Arctic summer ice loss is past tipping point - strong warming feedback and increase N hemisphere drought.
- Field research (caves) by A Vaks 2013 of huge region of permafrost in Siberia finds that global climates only slightly warmer than today are sufficient to thaw extensive regions of permafrost and the permafrost will be thawed at a warming of 1.5C.
-
Research in East Siberia of the El’gygytgyn meteorite impact crater shows that very degrees of Arctic summer warming (8C) have occurred in the past 3 million years at atmospheric CO2 concentrations around 300 ppm and this is due to Arctic feedbacks.
- All large Arctic amplifying feedbacks are operant - have been triggered.
- Satellite research shows a large increase in planetary methane emissions with Arctic methane emissions having increased 30% in 5 years.
- Atmospheric methane is since 2007 on a fast sustained increase due to planetary feedback emissions. Russian
- Ocean floor methane hydrate is destabilizing as the planet warms in at least three locations- East Siberian Arctic Shelf (2010). west of Arctic Svalbard Is (2009), and Eastern US (2012)
- Atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are far higher than the past 800,000 years- CO2 at 395 ppm 30% higher and methane at 1025 ppb over 110% higher
- Atmospheric greenhouse gas rate of increase is unprecedented
- Extreme weather events are already increasing on all continents
- Global and N hemisphere drought are both increasing
- Tropospheric ozone is increasing - global and N. hemisphere
- Ocean acidification rate is faster than past 3000 million years
- Ocean warming & acidification will destroy coral reefs in a matter of decades.
- Ocean plankton and phytoplankton algae in decline
- World GHG emission emissions are record high and increasing
- There is no integrated risk assessment.
- There is no full cost/full benefit analysis of energy conversion climate change mitigation
- Emissions mitigation scenarios delay zero carbon for 50 years or more
Today's emergency situation with respect to policy
- Governments and almost all scientists have bought into the idea of of the long standing 2C equilibrium policy limit applying only to 2100, so the planetary emergency has been made much worse.
- The World Bank issues a science report warning we are being committed to a 4C world.
- Policy (lack) has the world condemned to a literal end of the world the warming of 8C. Combined national emissions reduction pledges filed with the UN for the 2015 Paris Agreement commit us a 3.5C-4.6C warming by 2100 which is 6C-8C full stabilized equilibrium warming after 2100 (Climate Interactive).
- There is no agreed limit to GHG pollution globally or nationally - even though 350ppm is widely considered the limit for atmospheric CO2, and the UNFCCC requires a safe level of atmospheric GHGs.
- The only target is 2C which is certain global catastrophe - food, health, ecosystems, species and feedbacks. To make mattes much worse that 2C has been changed to 2C by 2100.
- The big economy States have delayed any new UN agreement to 2015 and delayed any actual new measures till 2020. There is no reason for any delay.
- There has been no change and no progress in the enormous subsidies governments give to the fossil fuel industry (over $US Triliion per year (IMF)
- All economy and energy plans globally and nationally are for increasing exploitation and combustion of fossil fuels.
- There is no price on GHG or carbon pollution and no pollution charges being applied.
IPCC on Atmospheric CO2 The recent rate of change is dramatic and unprecedented; increases in CO2 never exceeded 30 ppm in 1 kyr – yet now CO2 has risen by 30 ppm in just the last 17 years. (IPCC 2007 & FAQ 7) By any definition that is a planetary emergency.
The DARA 2012 2nd Climate Vulnerability Monitor report estimates that climate change causes 400,000 deaths on average each year today, mainly due to hunger and communicable diseases that affect above all children in developing countries.
Our present carbon-intensive energy system and related activities cause an estimated 4.5 million deaths each year linked to air pollution, hazardous occupations and cancer.
This is most definitely an emergency. Even more so when this death rate will greatly increase because global warming is committed to greatly increase.
Our present carbon-intensive energy system and related activities cause an estimated 4.5 million deaths each year linked to air pollution, hazardous occupations and cancer.
This is most definitely an emergency. Even more so when this death rate will greatly increase because global warming is committed to greatly increase.
An
Illustrated Guide to the Science of Global Warming Impacts: How We Know
Inaction Is the Gravest Threat Humanity Faces provides a very good
introduction, Joe
Romm Oct 14, 2012
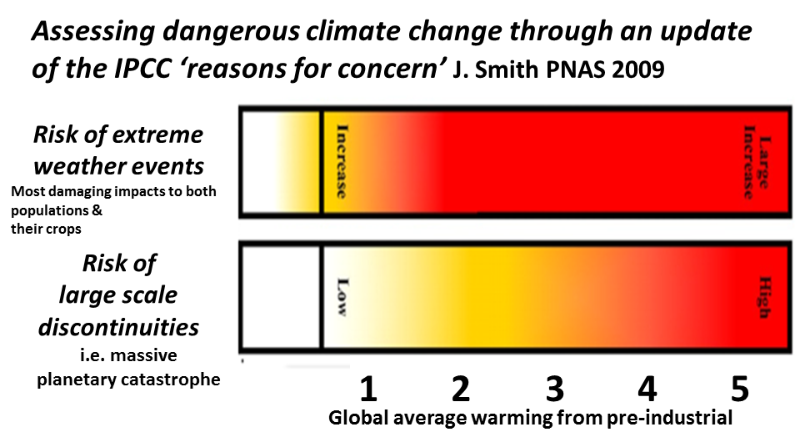
Comprehensive science assessments, like the 2007 AR4 IPCC assessment prove the 2C warming we have been targeting and the 3C that we are locked into, will be catastrophe for at least billions of people and catastrophe for world food production.
A 2011 paper Assessing dangerous climate change ... IPCC's ‘‘reasons for concern makes it obvious locked in warming puts us well into a extreme dangerous climate change emergency situation.
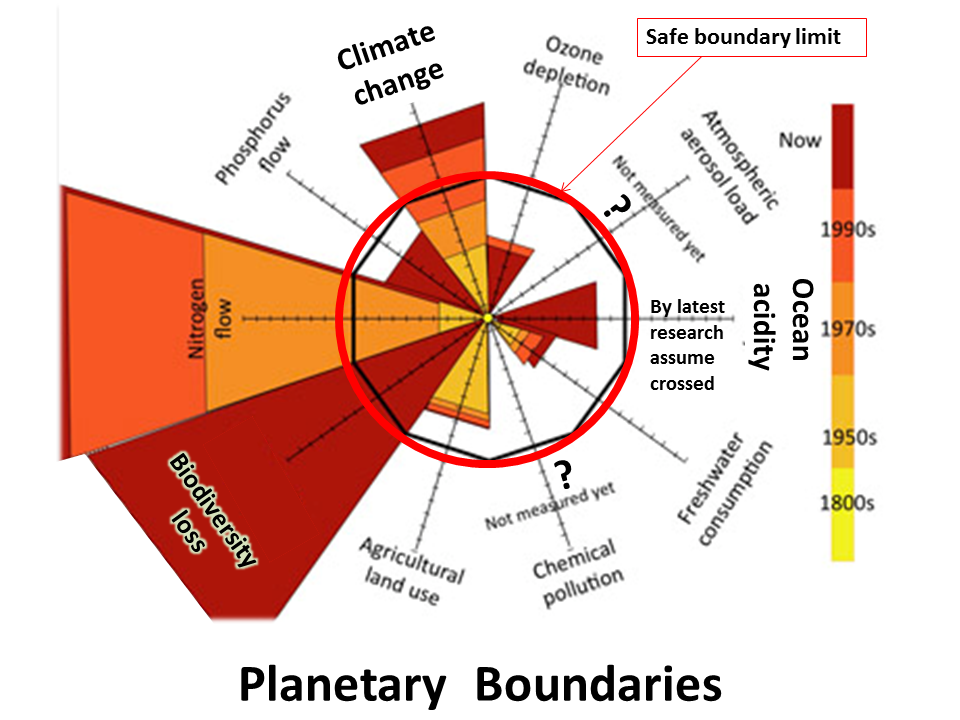
Published in 2009 a major research study on planetary boundaries that we must not cross found we have already crossed the limits on global climate change and biodiversity. To avoid catastrophic environmental change humanity must stay within defined 'planetary boundaries' for a range of essential Earth-system processes, says Johan Rockström and his co-authors in a Nature Feature. If one boundary is transgressed, then safe levels for other processes could also be under serious risk, they caution Nature special.. The assessment is published as Planetary Boundaries: Exploring the Safe Operating Space for Humanity The climate change boundary is one that has been crossed.
A 2011 paper Assessing dangerous climate change ... IPCC's ‘‘reasons for concern makes it obvious locked in warming puts us well into a extreme dangerous climate change emergency situation.
Published in 2009 a major research study on planetary boundaries that we must not cross found we have already crossed the limits on global climate change and biodiversity. To avoid catastrophic environmental change humanity must stay within defined 'planetary boundaries' for a range of essential Earth-system processes, says Johan Rockström and his co-authors in a Nature Feature. If one boundary is transgressed, then safe levels for other processes could also be under serious risk, they caution Nature special.. The assessment is published as Planetary Boundaries: Exploring the Safe Operating Space for Humanity The climate change boundary is one that has been crossed.
VIDEO James Hansen 2008. WE need to be at 300 ppm or less.
We are above 397 ppm CO2. As as Hansen repeated in 2012 after the big record sea ice drop, we are in a state of planetary emergency.
We are above 397 ppm CO2. As as Hansen repeated in 2012 after the big record sea ice drop, we are in a state of planetary emergency.
Emergency definition
- Russian researchers in 2013 have published 'Permafrost and the Destruction of Hydrates on the Shelf of East Arctic Seas as a Potential Cause of the “Methane Catastrophe”'. They conclude that the 'emission of methane from several areas of the Eastern Siberian Arctic Shelf is massive to the extent that growth in the methane concentrations in the atmosphere to values capable of causing a considerable and even catastrophic warning on the Earth is possible'.
- Unique in the field research of Siberian permafrost caves by A Vaks published 2013 has found that 'global climates only slightly warmer than today are sufficient to thaw extensive regions of permafrost'. At a global warming of 1.5C the vast region of permafrost is thawed.
- Unique in the field research published 2012 of a deep lake formed by a meteorite in Eastern Siberia has found that the Arctic (warming) is far more sensitive to atmospheric GHG global warming over the past 3 million years. The Arctic has warmed 8C in the Summer in response to atmospheric CO2 of 300-325 ppm.
Many reasons for planetary emergency
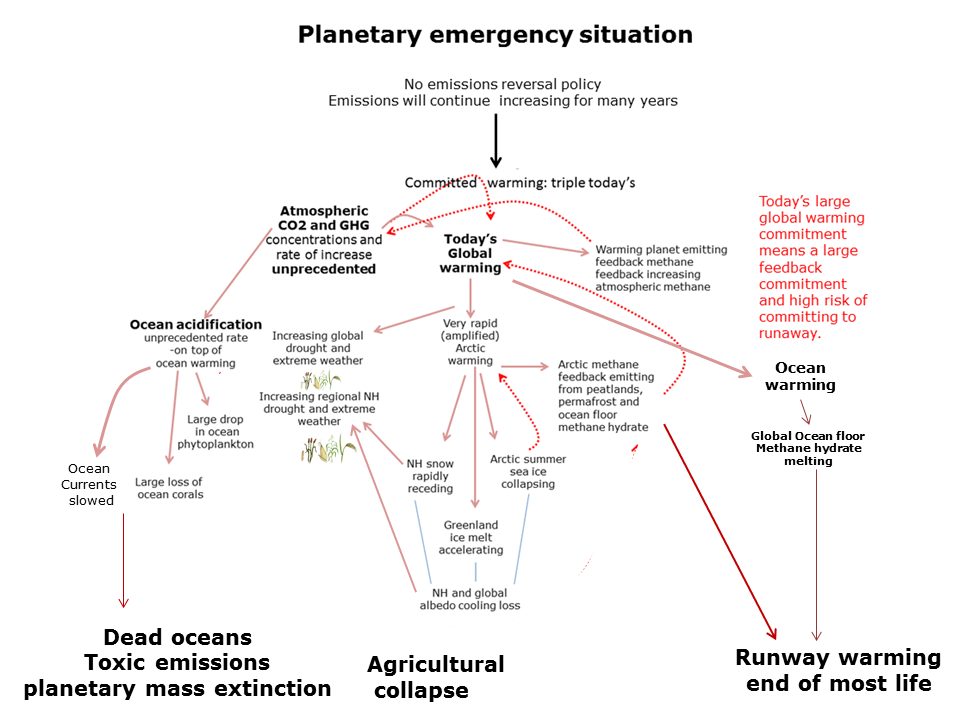
Above 2C Locked into disastrous global climate change. The overriding reason why we are in a global climate change emergency is the total amount of future warming and climate change that we are already locked into, or committed to in climate science terminology. Without a drastic planetary emergency response now, we cannot avoid a warming of over 3C by 2100. A 2013 World Bank report warns we are locking ourselves into a warming of 4C.
At least 6C by 2100. Since 2008 the International Energy Agency has been warning we are fixed on a world economy fossil fuel energy track that takes us to at least 6C by 2100.
At least 6C by 2100. Since 2008 the International Energy Agency has been warning we are fixed on a world economy fossil fuel energy track that takes us to at least 6C by 2100.
The 2C Target
James Hansen has said 2C is disastrous and has published explaining 1C is now the danger limit, with 17 experts who co-author the paper (Assessing ‘‘Dangerous Climate Change’’: Required Reduction of Carbon Emissions to Protect Young People, Future Generations and Nature) 2C is accepted as the climate policy target, though a mojority of UN Convention nation Parties correctly want under 1.5C for their very survival.
However to make matters far worse, unannounced the 2C limit has been changed, from the full very long term equilibrium warming to a 2C limit only by 2100. Any warming target obviously must be the stabliized equilibrium temperature. For 2C by 2100 that is in fact a full limit of 3.5C after 2100, due to the ocean heat lag. The national UN pledges (even all carried out) puts the world at 3.5C-4.6 by 2100, which is 6C-8C long after 2100 (Climate Interactive 28 Sept 2015). These are unlivable temperature increases.
James Hansen has said 2C is disastrous and has published explaining 1C is now the danger limit, with 17 experts who co-author the paper (Assessing ‘‘Dangerous Climate Change’’: Required Reduction of Carbon Emissions to Protect Young People, Future Generations and Nature) 2C is accepted as the climate policy target, though a mojority of UN Convention nation Parties correctly want under 1.5C for their very survival.
However to make matters far worse, unannounced the 2C limit has been changed, from the full very long term equilibrium warming to a 2C limit only by 2100. Any warming target obviously must be the stabliized equilibrium temperature. For 2C by 2100 that is in fact a full limit of 3.5C after 2100, due to the ocean heat lag. The national UN pledges (even all carried out) puts the world at 3.5C-4.6 by 2100, which is 6C-8C long after 2100 (Climate Interactive 28 Sept 2015). These are unlivable temperature increases.
Too late to avoid going far above 2C. Leading world climate change science advisor warns climate target 'out the window 'BBC News 23 Aug 2012.
Professor Sir Robert Watson said that the hope of restricting the average temperature rise to 2C was "out the window".
He said that the likely rise is 3 to 4C and may be as high as 5C - with dire consequences.
He presented the situation to the 2012 American Geophysical Union conference. With an radical drastic emergency response it is theoretically possible to keep under 2C but Robert Watson's prediction was based on the reality there will be no such response because the national pledges made are so paltry.
By definition any risk of not stabilizing below 2C is a climate planetary emergency.
By definition any risk of not stabilizing below 2C is a climate planetary emergency.
All global GHG emissions are rising at record levels
Despite a 2014 slowing in the rate of CO2 increase, these are extremely fast rates. Emissions have to be zero so today's massive annual emissions 10GtC/billion tonnes of carbon keeps us on a fast track to planetary catastrophe.
Incredibly despite the above
o There is no indication of any great government, public or expert alarm over the situation
o Since the failed 2009 Copenhagen UN climate summit the focus has switched from emissions reduction to adaptation.
o The only agreed climate change limit is the 1996 EU policy of 2C. It is now obvious 2C is catastrophe., yet it remains almost universally supported.g
o The international agenda is for no change to the situation till after 2010.
o There is no world agreement or even a plan to reduce emissions.
o UN negotiations on emissions are on hold till after 2015 with a view to a post 2020 climate agenda.
o The combined national UN emissions emissions pledges are a commitment to a warming of 4.5C by 2100 (Climate Interactive)
o The only plan is to keep increasing fossil fuel production and combustion
o There is no plan to reduce CO2 or methane and reducing nitrous oxide emissions is not even being considered.
o The locked in (practically unavoidable) global warming commitment is several times today's warming of 0.8C.
o The global temperature and ocean acidification cannot stop increasing without all industrial carbon emissions
stopping (zero carbon) and there is no plan or target to do so.
o Global warming and ocean acidification last 1000s of years
o There is no indication of any great government, public or expert alarm over the situation
o Since the failed 2009 Copenhagen UN climate summit the focus has switched from emissions reduction to adaptation.
o The only agreed climate change limit is the 1996 EU policy of 2C. It is now obvious 2C is catastrophe., yet it remains almost universally supported.g
o The international agenda is for no change to the situation till after 2010.
o There is no world agreement or even a plan to reduce emissions.
o UN negotiations on emissions are on hold till after 2015 with a view to a post 2020 climate agenda.
o The combined national UN emissions emissions pledges are a commitment to a warming of 4.5C by 2100 (Climate Interactive)
o The only plan is to keep increasing fossil fuel production and combustion
o There is no plan to reduce CO2 or methane and reducing nitrous oxide emissions is not even being considered.
o The locked in (practically unavoidable) global warming commitment is several times today's warming of 0.8C.
o The global temperature and ocean acidification cannot stop increasing without all industrial carbon emissions
stopping (zero carbon) and there is no plan or target to do so.
o Global warming and ocean acidification last 1000s of years
There is a very long list of very damaging global climate change effects. People will be aware of a big increase in all kinds of extreme weather impacts over the past decade, which has dramatically demonstrated how this category of global climate change impacts is the most damaging to human populations and to their food crops. These have all been caused by a global warming of 0.8C, but we are committed (locked in) to a future warming several times today's- without an emergency response now. It is impossible to adapt to all these interacting increasing impacts- though we are bound to try.
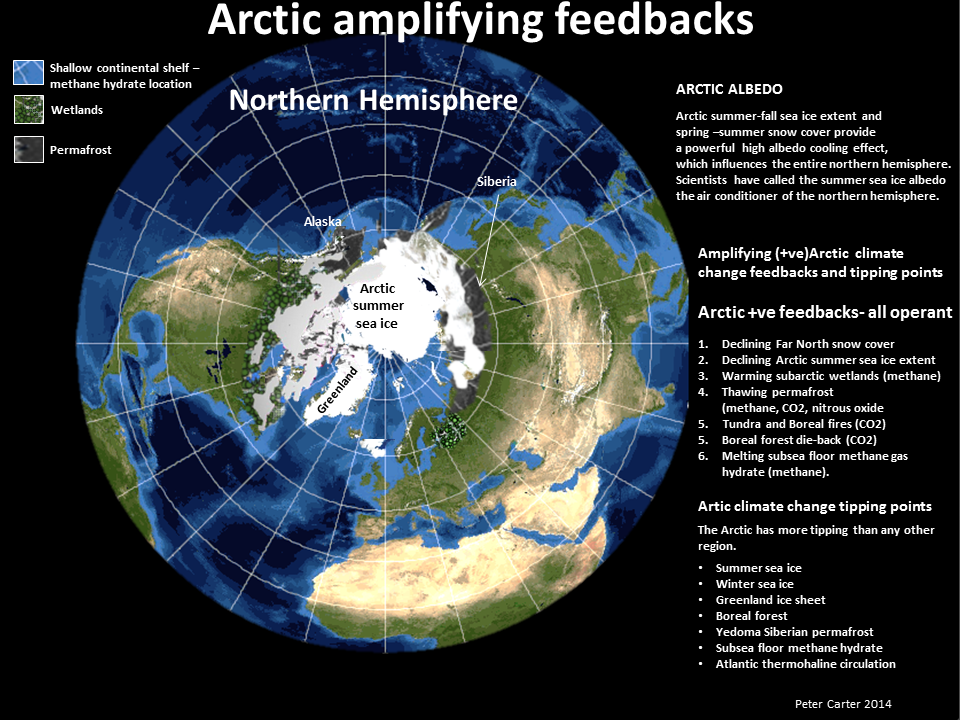
Arctic planetary emergency
o Snow and sea ice melt
o Methane feedback emissions
o Runaway global heating
o Snow and sea ice melt
o Methane feedback emissions
o Runaway global heating
Commitment / 'locking in' to
catastrophic impacts, at risk of runaway due to multiple
slow feedback climate sensitivity
catastrophic impacts, at risk of runaway due to multiple
slow feedback climate sensitivity
Global water & food insecurity & insufficiency
Increasing crop losses
all best agricultural regions
from heat, drought & floods
from heat, drought & floods
Long list of the general emergency reasons that proves we are all in a dire planetary emergency and must all push hard for an emergency response.
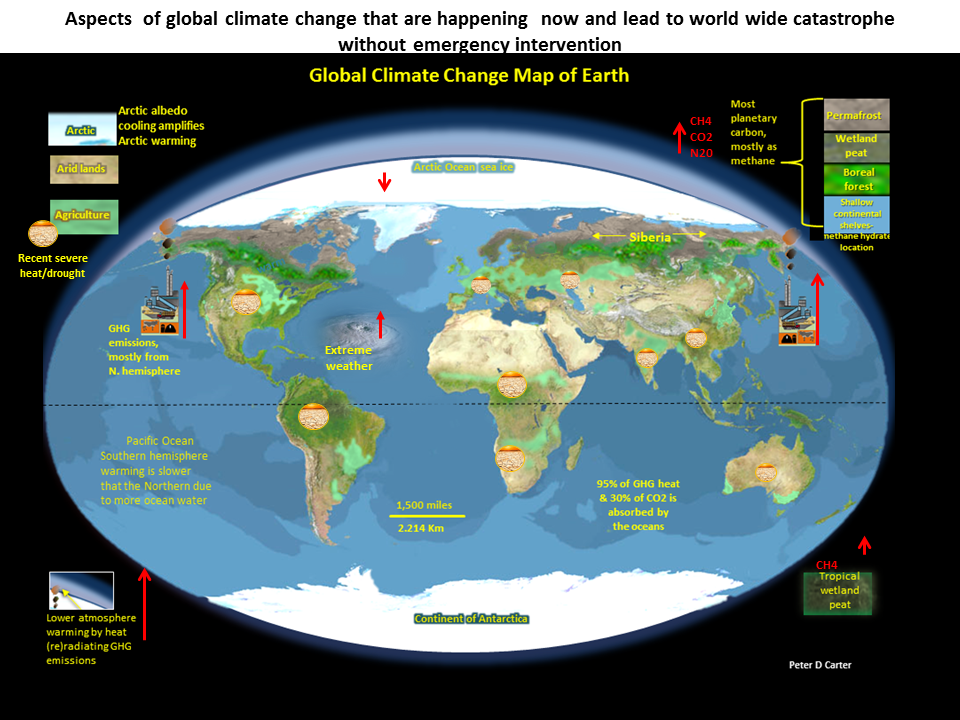
Worst climate catastrophes in the making
o World food production decline, affecting almost
all main producing regions
o Increasing extreme weather
o Arctic multiple amplifying feedbacks
o Deep ocean warming leading to methane release from subsea floor gas hydrate
o Dying oceans- warming +deoxygenation +acidification
o Amazon collapse
o Mass extinction of almost all life
o World food production decline, affecting almost
all main producing regions
o Increasing extreme weather
o Arctic multiple amplifying feedbacks
o Deep ocean warming leading to methane release from subsea floor gas hydrate
o Dying oceans- warming +deoxygenation +acidification
o Amazon collapse
o Mass extinction of almost all life
o Ice
sheet destabilization - sea level rise
Though as a catastrophe it is far from the worst, wee could already be committed to 20 meters or 70 feet.
The Greenland melt is accelerating.
The West Antarctic ice sheet is in irreversible collapse.
Now research finds (8 Aug 2013) that the East Antarctic ice sheet (the largest) may be vulnerable to warming.
Though as a catastrophe it is far from the worst, wee could already be committed to 20 meters or 70 feet.
The Greenland melt is accelerating.
The West Antarctic ice sheet is in irreversible collapse.
Now research finds (8 Aug 2013) that the East Antarctic ice sheet (the largest) may be vulnerable to warming.
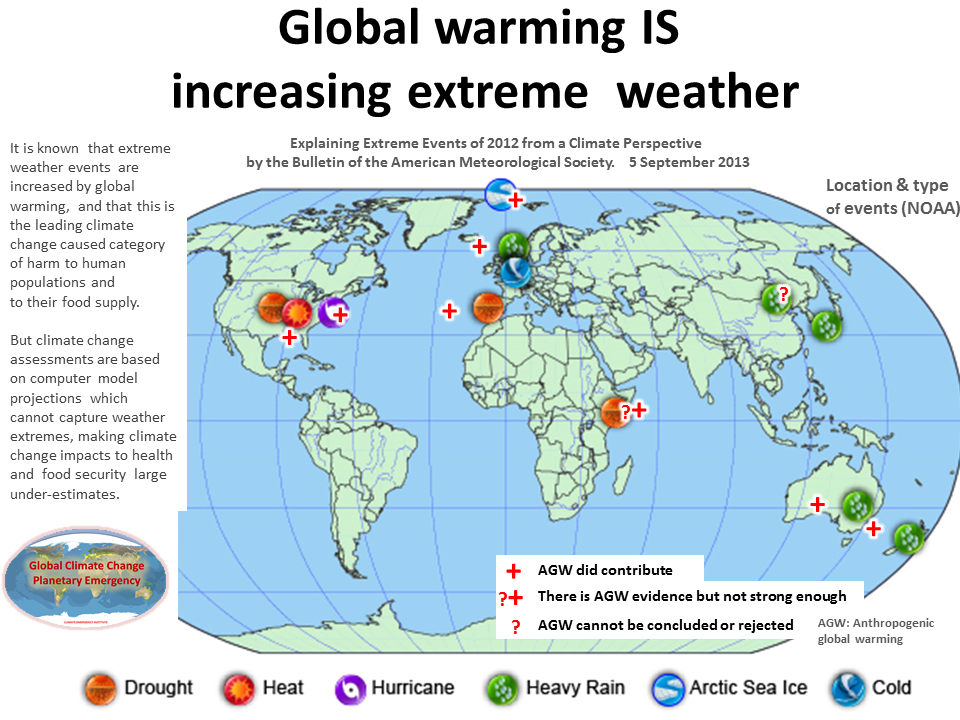
While multiple lines of evidence make it overwhelmingly clear that we are all in a planetary emergency situation (James Hansen 2008 , 2012), governments continue to delay any new UN measures to slow-stop GHG emissions, and assessments do not address the worst impacts and most catastrophic dangers.
Why Global Warming Will Be Far Worse, Far Sooner, John Atcheson Sept 2013
Why Global Warming Will Be Far Worse, Far Sooner, John Atcheson Sept 2013
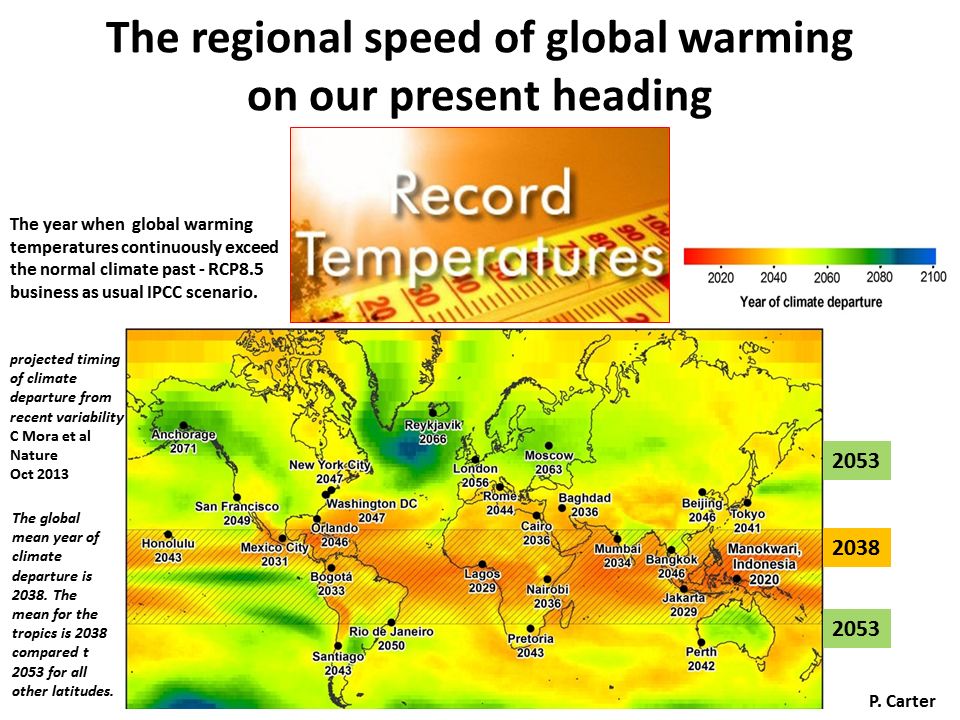
Study in Nature (Oct 2013) Reveals Urgent New Time Frame for Climate Change
From PDF Areas in the tropics are projected to experience unprecedented climates first – within the next decade. Under a business-as-usual scenario, the index shows the average location on Earth will experience a radically different climate by 2047. Other papers with similar findings
From PDF Areas in the tropics are projected to experience unprecedented climates first – within the next decade. Under a business-as-usual scenario, the index shows the average location on Earth will experience a radically different climate by 2047. Other papers with similar findings

CLIMATE EMERGENCY INSTITUTE
The health and human rights approach to climate change
The health and human rights approach to climate change
New research
by date
2 Sept 2020 Arctic heating races ahead of worst case estimates
31 August 2020 Sea level rise from ice sheets track worst-case climate change scenario
3 August 2020, PNAS, C. R. Schwalm, RCP8.5 tracks cumulative CO2 emission (Worst-case)
1 June 2020 Atmospheric CO2 highest in 23 million years
2 Sept 2020 Arctic heating races ahead of worst case estimates
31 August 2020 Sea level rise from ice sheets track worst-case climate change scenario
3 August 2020, PNAS, C. R. Schwalm, RCP8.5 tracks cumulative CO2 emission (Worst-case)
1 June 2020 Atmospheric CO2 highest in 23 million years
5 Mar 2020 Emissions: world has four times the work or one-third of the time
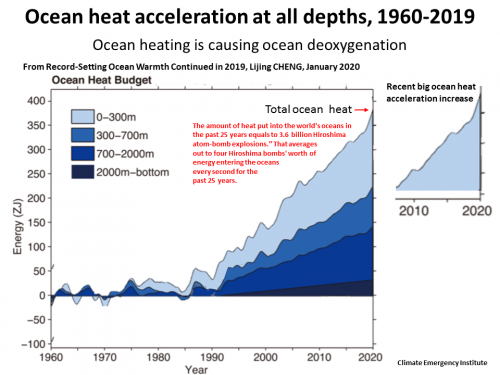
13 Jan 2010 Record-Setting Ocean Warmth Continued in 2019
Dec 2019 UN climate emergency COP25
13 Jan 2010 Record-Setting Ocean Warmth Continued in 2019
Dec 2019 UN climate emergency COP25
29 Oct 2019 New data triple estimates of global vulnerability to sea-level rise and coastal flooding 200M 2050 480M 2100
8 April 2019 Global warming is shrinking glaciers faster than thought (non ice-sheet). Global glacier mass changes...
Nov 2017 EDF Conflict & Refugees , 10s of millions in 10 years
Dec 2016 Arctic report card Arctic has switched from carbon sink to carbon source
Mar 21 2016. Anthropogenic carbon release rate unprecedented (10X faster) during the past 66 million year
21 March 2016 T. Lenton. Risk of multiple interacting tipping points should encourage rapid CO2 emission reduction
21 Mar 2016 Zeebe Anthropogenic carbon release rate unprecedented (10X faster) during the past 66 million years
5 Feb 2016 Global mismatch between greenhouse gas emissions and the burden of climate change
14 Oct 2015 Uncertainty makes action on climate change more – not less – urgent
14 Oct 2015 Bubble plumes off Washington, Oregon suggest warmer ocean may be releasing frozen methane
12 Oct 2015 Global marine analysis suggests food chain collapse
23 Sept 2015 Ocean phytoplankton algae in decline
21 Sept 2015 Economic analysis $300 Trillion + $43 Trillion from permafrost economic damage
4 Aug 2015 Accelerating global glacier melt 'unprecedented'.
14 July 2015 Continued destruction of Earth's plant life places humans in jeopardy Basic science
June 2015 Food shortage to trigger global collapse by 2040 under current policies
27 May 2015 Monbiot on science of past mega extinctions
9 April 2015 Triassic mass extinction may give clues on how oceans will be affected by climate change
24 March 2015 N. Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation slow down already
March 2015 IPCC expert says 2-Degree Global Warming Target 'Utterly Inadequate'
Mar 2015 East Antarctic ice sheets also vulnerable to accelerated melting
Mar 2015 Sc. Am. CO2 400ppm 20 million years level
Mar 2015B. Cook Unprecedented
21st century drought risk American Southwest & Central Plains
March 2015 Shell-shocked: Ocean acidification likely hampers tiny shell builders in Southern Ocean shell making 24% decline large areas S. Ocean 17 yrs.
Mar 2015 T. S. Lontzek Stochastic integrated assessment of climate tipping points indicates the need for strict climate policy
Mar 2015 R. Brienen
Long-term decline of the Amazon carbon sink (less CO2 uptake)
Mar 2015 Drought impact on forest carbon- in Amazonia
Reduced uptake
Mar 2015 S. Smith
Near-term acceleration in rate of temperature change 40 yr period
Mar 2015 C. Koven Permafrost carbon−climate feedback is sensitive to deep soil carbon big +ve
Mar 2015 S. Rahmstorf.
Exceptional twentieth-century slowdown in MOC Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation
Feb 2015 B. Cook
Unprecedented 21st century drought risk American Southwest & Central Plains
Feb 2015 IPCC sea-level rise scenarios not fit for purpose for high-risk coastal areas
Jan 2015 U Exeter Global warming doubles risk of extreme La Niña event, research shows
Jan 2015 Will Steffen Planetary Boundaries
Nearly half the systems crucial to stability of planet compromised
Jan 2015 T. Webb
Global Patterns of Extinction Risk in Marine and Non-marine Systems.20-25 % of the well-known species in our seas are now threatened with extinction -- the same figure as land living plants and animals.
Jan 2015 S. Asseng Rising temperatures reduce global wheat production
Dec 2014 Maximum warming occurs about one decade after a CO2 emission. last >100 yrs.
Dec 2014 Scott Robeson Trends in hemispheric warm and cold anomalies Both extremes increasing
Dec 2014 NASA Satellites measure increase of Sun's energy absorbed in the Arctic=+feedback
Dec 2014 D. Griffin How unusual is the 2012–2014 California drought? worst in 1200 yrs
Dec 2014 Adrian Schilt, Nitrous oxide deglaciation - rose at end of last ice age response to warming
Nov 2014 N.J. Silbiger Reefs shift from net accretion to net erosion... Acid. eroding reef skeletons, as well as reducing growth
Nov 2014 How emissions, climate, will impact mid-century air quality USA M. Martin Future ozone levels could cause serious damage to plants and crops, even if emissions are cut
Nov 2014 D. Levitan Bleaching Long-term reduced spawning coral species due to temperature stress
Nov 2014 World Bank Some climate change impacts unavoidable: World Bank 3rd climate report
BMJ Oct 2014 WHO should declare health emergency
Oct 2014 Quantifying underestimates of long-term upper-ocean warming
SH underestimated
by 24-58%
IPCC Risk of warming up to an unlivable 7.8°C by 2100
Without additional efforts to reduce GHG emissions , ... with a range to 7.8°C including climate uncertainty. (IPCC AR5 WG3 SPM p8).
Oct 2014 T. Hilker Vegetation dynamics and rainfall sensitivity of the Amazon- large drying loss & to continue FB
Sept 2014 Noah Diffenbaugh
California drought linked to climate change Stanford
Sept 2014 WMO 2013 Record GHG levels impact atmosphere and oceans, Increased fastest rate record (1984)-possible reduced land uptake Extreme weather increasing from AGWarming
Sept 2014 Global Carbon Project record CO2 emissions 9.9±0.5 GtC (billion tonnes of carbon) (36 GtCO2) emitted to the atmosphere, 61% above 1990. Atmospheric CO2 growth rate increased
Sept 2014 Amazon’s ‘flying rivers’ dry up as historic drought takes hold. 2015 drought deeepening
Sep 2014 M.Goulden
Sierra Nevada freshwater runoff could drop 26 percent by 2100- even less water availability
Sept 2014 M. Bougamont (more) Sensitive response of Greenland Ice Sheet to surface melt. Also to extremes
Sept 2014 Warning times for species extinctions due to climate change Better risk assess.
Lancet 20.9.2014 Some climate change impacts unavoidable: World Bank Health risks of climate change: act now or pay later
Aug 2014 Yi-Chun Chen. Satellite estimate of global aerosol–cloud radiative forcing (cooling) by marine warm clouds.Total impact influence of aerosols on cloud is almost double IPCC
Aug 2014 Assessing the risk of persistent drought T. Ault (US SW) Decade drought at least 50 percent,Mega 20-50%
Aug 2014 Incredible' rate of polar ice loss. The rate of loss of ice from the two regions has more than doubled since 2009
Aug 2014 S. Davis Commitment accounting of CO2
emissions Existing power plants 300 billion more tons CO2
Aug 2014 B. Marzeion,
Attribution of global glacier mass loss to anthropogenic-causes
Accelerating
July 2014 Eui-Seok Chung Upper-tropospheric moistening in response to anthrop. warming. + Feedback
July 2014 Amos Tai Threat to future global food security from climate change and ozone air pollution.
July 2014 IPCC excessive governmental intrusion in the process.
July 2014 M. Raupach. The declining uptake rate of atmospheric CO2 by lan d and ocean sinks
July 2014 D. Lobell Getting caught with our plants down: the risks of a global crop yield slowdown from climate trends in the next two decades
10% yield loss has increased from a less than 1 in 200 chance arising from internal climate variability alone, to a 1 in 10 chance for maize and 1 in 20 chance for wheat.
June 2014 Greenland tipping point another 1C- committed by committed warming
June 2014 Miroslav Trnka Adverse weather conditions for European wheat production will become more frequent with climate change.similar risk other crops.
June 2014 Below 2°C or 1.5°C depends on rapid action from all countries
May 2014 Devastating human impact on the Amazon rainforest Logging and surface wildfires 54 billion tonnes of carbon/yr Brazilian Amazon, Rika Berenguer A Large-Scale Field Assessment of Carbon Stocks in Human-Modified Tropical Forests
May 2014 West Antarctic ice sheet is collapsing
May 2014 Uncorking East Antarctica could yield unstoppable sea-level rise. M Mengel PKI Ice plug prevents irreversible discharge from East Antarctica.
May 2014 Filippo Ferrario The effectiveness of coral reefs for coastal hazard risk reduction and adaptation
May 2014 Guillem Chust Phytoplankton & zooplankton to decrease by 6% & 11% by 2100
Extreme rapid glacial melt down
Everest shrinking Tibetan ice plateau decapitated
April 2014 Abrupt increases in Amazonian tree mortality due to drought–fire interactions-beyond tipping point.
April 2014 Liming Zhou. Widespread decline of Congo rainforest greenness past decade (drying)
April 2014 S. Lewandowsky
Scientific uncertainty and climate change+ urgent mitigation 2 parts
April 2014 M. Turetsky Wetlands causing atmospheric methane increase.
April 2014 Heidi Kreibich (fuller) Costing Natural Hazards
April 2014 Don't wait till you feel it. K. Ricke Natural climate variability and future climate policy.
Mar 2014 B Cook Global warming and 21st century drying. To 30% of planet, major food regions
Mar 2014 g. Yvon-Durocher, Methane emissions will leap as Earth warms Several X /degree C
Mar 2014 CAGE - Center Arctic Gas Hydrate, Climate & Environment.Methane is leaking from permafrost offshore Siberia) methane hydrate)
Feb 2014 Frank T. Princiotta Urgent mitigation Global climate change: The quantifiable sustainability challenge
Dec 2013 J. Hansen Assessing Dangerous climate change. Limit is 1.0C
Feb 2012 A Levermann PKI Potential climatic transitions with profound impact
on Europe
2010 Dramatic climate change is unpredictable
P.D. Ditlevsen
Tipping points: Early warning and wishful thinking.
27 April 2008 Zeebe & CaldieraIndustrial CO2 emissions are being added to the atmosphere 14,000 X faster than can be removed.
2007 IPCC Impacts unprecedented in hundreds of thousands of years
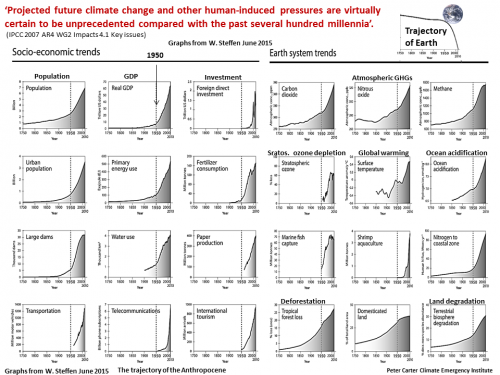
Projected future climate change and other human-induced pressures are virtually certain to be unprecedented compared with the past several hundred millennia (IPCC AR4 2007 2007 Working Group II Impacts 4.1 Key issues)
2007 IPCC
Unprecedented increase in atmospheric CO2
The recent rate of change [atmospheric CO2] is dramatic and unprecedented; increases in CO2 never exceeded 30 ppm in 1 kyr – yet now CO2 has risen by 30 ppm in just the last 17 years. (IPCC AR4 2007 WG1 Science FAQ 7.1)
8 April 2019 Global warming is shrinking glaciers faster than thought (non ice-sheet). Global glacier mass changes...
Nov 2017 EDF Conflict & Refugees , 10s of millions in 10 years
Dec 2016 Arctic report card Arctic has switched from carbon sink to carbon source
Mar 21 2016. Anthropogenic carbon release rate unprecedented (10X faster) during the past 66 million year
21 March 2016 T. Lenton. Risk of multiple interacting tipping points should encourage rapid CO2 emission reduction
21 Mar 2016 Zeebe Anthropogenic carbon release rate unprecedented (10X faster) during the past 66 million years
5 Feb 2016 Global mismatch between greenhouse gas emissions and the burden of climate change
14 Oct 2015 Uncertainty makes action on climate change more – not less – urgent
14 Oct 2015 Bubble plumes off Washington, Oregon suggest warmer ocean may be releasing frozen methane
12 Oct 2015 Global marine analysis suggests food chain collapse
23 Sept 2015 Ocean phytoplankton algae in decline
21 Sept 2015 Economic analysis $300 Trillion + $43 Trillion from permafrost economic damage
4 Aug 2015 Accelerating global glacier melt 'unprecedented'.
14 July 2015 Continued destruction of Earth's plant life places humans in jeopardy Basic science
June 2015 Food shortage to trigger global collapse by 2040 under current policies
27 May 2015 Monbiot on science of past mega extinctions
9 April 2015 Triassic mass extinction may give clues on how oceans will be affected by climate change
24 March 2015 N. Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation slow down already
March 2015 IPCC expert says 2-Degree Global Warming Target 'Utterly Inadequate'
Mar 2015 East Antarctic ice sheets also vulnerable to accelerated melting
Mar 2015 Sc. Am. CO2 400ppm 20 million years level
Mar 2015B. Cook Unprecedented
21st century drought risk American Southwest & Central Plains
March 2015 Shell-shocked: Ocean acidification likely hampers tiny shell builders in Southern Ocean shell making 24% decline large areas S. Ocean 17 yrs.
Mar 2015 T. S. Lontzek Stochastic integrated assessment of climate tipping points indicates the need for strict climate policy
Mar 2015 R. Brienen
Long-term decline of the Amazon carbon sink (less CO2 uptake)
Mar 2015 Drought impact on forest carbon- in Amazonia
Reduced uptake
Mar 2015 S. Smith
Near-term acceleration in rate of temperature change 40 yr period
Mar 2015 C. Koven Permafrost carbon−climate feedback is sensitive to deep soil carbon big +ve
Mar 2015 S. Rahmstorf.
Exceptional twentieth-century slowdown in MOC Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation
Feb 2015 B. Cook
Unprecedented 21st century drought risk American Southwest & Central Plains
Feb 2015 IPCC sea-level rise scenarios not fit for purpose for high-risk coastal areas
Jan 2015 U Exeter Global warming doubles risk of extreme La Niña event, research shows
Jan 2015 Will Steffen Planetary Boundaries
Nearly half the systems crucial to stability of planet compromised
Jan 2015 T. Webb
Global Patterns of Extinction Risk in Marine and Non-marine Systems.20-25 % of the well-known species in our seas are now threatened with extinction -- the same figure as land living plants and animals.
Jan 2015 S. Asseng Rising temperatures reduce global wheat production
Dec 2014 Maximum warming occurs about one decade after a CO2 emission. last >100 yrs.
Dec 2014 Scott Robeson Trends in hemispheric warm and cold anomalies Both extremes increasing
Dec 2014 NASA Satellites measure increase of Sun's energy absorbed in the Arctic=+feedback
Dec 2014 D. Griffin How unusual is the 2012–2014 California drought? worst in 1200 yrs
Dec 2014 Adrian Schilt, Nitrous oxide deglaciation - rose at end of last ice age response to warming
Nov 2014 N.J. Silbiger Reefs shift from net accretion to net erosion... Acid. eroding reef skeletons, as well as reducing growth
Nov 2014 How emissions, climate, will impact mid-century air quality USA M. Martin Future ozone levels could cause serious damage to plants and crops, even if emissions are cut
Nov 2014 D. Levitan Bleaching Long-term reduced spawning coral species due to temperature stress
Nov 2014 World Bank Some climate change impacts unavoidable: World Bank 3rd climate report
BMJ Oct 2014 WHO should declare health emergency
Oct 2014 Quantifying underestimates of long-term upper-ocean warming
SH underestimated
by 24-58%
IPCC Risk of warming up to an unlivable 7.8°C by 2100
Without additional efforts to reduce GHG emissions , ... with a range to 7.8°C including climate uncertainty. (IPCC AR5 WG3 SPM p8).
Oct 2014 T. Hilker Vegetation dynamics and rainfall sensitivity of the Amazon- large drying loss & to continue FB
Sept 2014 Noah Diffenbaugh
California drought linked to climate change Stanford
Sept 2014 WMO 2013 Record GHG levels impact atmosphere and oceans, Increased fastest rate record (1984)-possible reduced land uptake Extreme weather increasing from AGWarming
Sept 2014 Global Carbon Project record CO2 emissions 9.9±0.5 GtC (billion tonnes of carbon) (36 GtCO2) emitted to the atmosphere, 61% above 1990. Atmospheric CO2 growth rate increased
Sept 2014 Amazon’s ‘flying rivers’ dry up as historic drought takes hold. 2015 drought deeepening
Sep 2014 M.Goulden
Sierra Nevada freshwater runoff could drop 26 percent by 2100- even less water availability
Sept 2014 M. Bougamont (more) Sensitive response of Greenland Ice Sheet to surface melt. Also to extremes
Sept 2014 Warning times for species extinctions due to climate change Better risk assess.
Lancet 20.9.2014 Some climate change impacts unavoidable: World Bank Health risks of climate change: act now or pay later
Aug 2014 Yi-Chun Chen. Satellite estimate of global aerosol–cloud radiative forcing (cooling) by marine warm clouds.Total impact influence of aerosols on cloud is almost double IPCC
Aug 2014 Assessing the risk of persistent drought T. Ault (US SW) Decade drought at least 50 percent,Mega 20-50%
Aug 2014 Incredible' rate of polar ice loss. The rate of loss of ice from the two regions has more than doubled since 2009
Aug 2014 S. Davis Commitment accounting of CO2
emissions Existing power plants 300 billion more tons CO2
Aug 2014 B. Marzeion,
Attribution of global glacier mass loss to anthropogenic-causes
Accelerating
July 2014 Eui-Seok Chung Upper-tropospheric moistening in response to anthrop. warming. + Feedback
July 2014 Amos Tai Threat to future global food security from climate change and ozone air pollution.
July 2014 IPCC excessive governmental intrusion in the process.
July 2014 M. Raupach. The declining uptake rate of atmospheric CO2 by lan d and ocean sinks
July 2014 D. Lobell Getting caught with our plants down: the risks of a global crop yield slowdown from climate trends in the next two decades
10% yield loss has increased from a less than 1 in 200 chance arising from internal climate variability alone, to a 1 in 10 chance for maize and 1 in 20 chance for wheat.
June 2014 Greenland tipping point another 1C- committed by committed warming
June 2014 Miroslav Trnka Adverse weather conditions for European wheat production will become more frequent with climate change.similar risk other crops.
June 2014 Below 2°C or 1.5°C depends on rapid action from all countries
May 2014 Devastating human impact on the Amazon rainforest Logging and surface wildfires 54 billion tonnes of carbon/yr Brazilian Amazon, Rika Berenguer A Large-Scale Field Assessment of Carbon Stocks in Human-Modified Tropical Forests
May 2014 West Antarctic ice sheet is collapsing
May 2014 Uncorking East Antarctica could yield unstoppable sea-level rise. M Mengel PKI Ice plug prevents irreversible discharge from East Antarctica.
May 2014 Filippo Ferrario The effectiveness of coral reefs for coastal hazard risk reduction and adaptation
May 2014 Guillem Chust Phytoplankton & zooplankton to decrease by 6% & 11% by 2100
Extreme rapid glacial melt down
Everest shrinking Tibetan ice plateau decapitated
April 2014 Abrupt increases in Amazonian tree mortality due to drought–fire interactions-beyond tipping point.
April 2014 Liming Zhou. Widespread decline of Congo rainforest greenness past decade (drying)
April 2014 S. Lewandowsky
Scientific uncertainty and climate change+ urgent mitigation 2 parts
April 2014 M. Turetsky Wetlands causing atmospheric methane increase.
April 2014 Heidi Kreibich (fuller) Costing Natural Hazards
April 2014 Don't wait till you feel it. K. Ricke Natural climate variability and future climate policy.
Mar 2014 B Cook Global warming and 21st century drying. To 30% of planet, major food regions
Mar 2014 g. Yvon-Durocher, Methane emissions will leap as Earth warms Several X /degree C
Mar 2014 CAGE - Center Arctic Gas Hydrate, Climate & Environment.Methane is leaking from permafrost offshore Siberia) methane hydrate)
Feb 2014 Frank T. Princiotta Urgent mitigation Global climate change: The quantifiable sustainability challenge
Dec 2013 J. Hansen Assessing Dangerous climate change. Limit is 1.0C
Feb 2012 A Levermann PKI Potential climatic transitions with profound impact
on Europe
2010 Dramatic climate change is unpredictable
P.D. Ditlevsen
Tipping points: Early warning and wishful thinking.
27 April 2008 Zeebe & CaldieraIndustrial CO2 emissions are being added to the atmosphere 14,000 X faster than can be removed.
2007 IPCC Impacts unprecedented in hundreds of thousands of years
Projected future climate change and other human-induced pressures are virtually certain to be unprecedented compared with the past several hundred millennia (IPCC AR4 2007 2007 Working Group II Impacts 4.1 Key issues)
2007 IPCC
Unprecedented increase in atmospheric CO2
The recent rate of change [atmospheric CO2] is dramatic and unprecedented; increases in CO2 never exceeded 30 ppm in 1 kyr – yet now CO2 has risen by 30 ppm in just the last 17 years. (IPCC AR4 2007 WG1 Science FAQ 7.1)
May 2014 West Antarctic ice sheetin irreversible collapse.
2014 Federal assessment
Disastrous climate
for the USA
Disastrous climate
for the USA
1 June 2020 Atmospheric carbon dioxide levels greater than 23 million-year record.
IPCC AR5 2014 plantary emergency in one chart
Global climate change
is already killing hundreds of thousands DARA 2012
is already killing hundreds of thousands DARA 2012
Increasing worldwide disastrous climate change impacts already, and far greater committed (locked in) climate change should make the emergency obvious.
Global warming rate
is at least
10X faster than the
past 65 Million yrs
is at least
10X faster than the
past 65 Million yrs
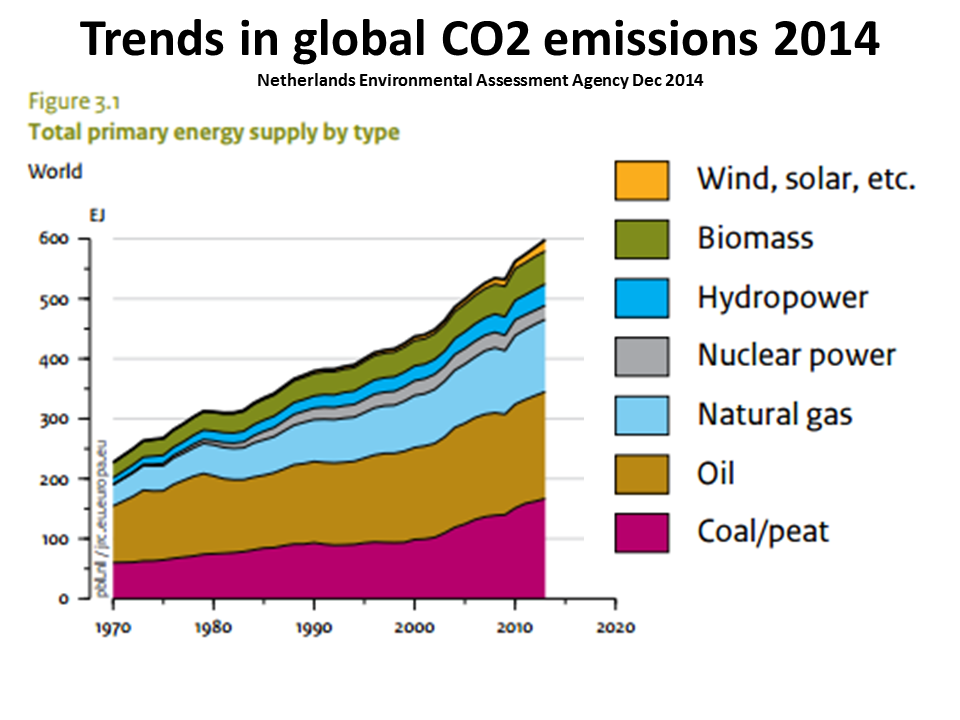
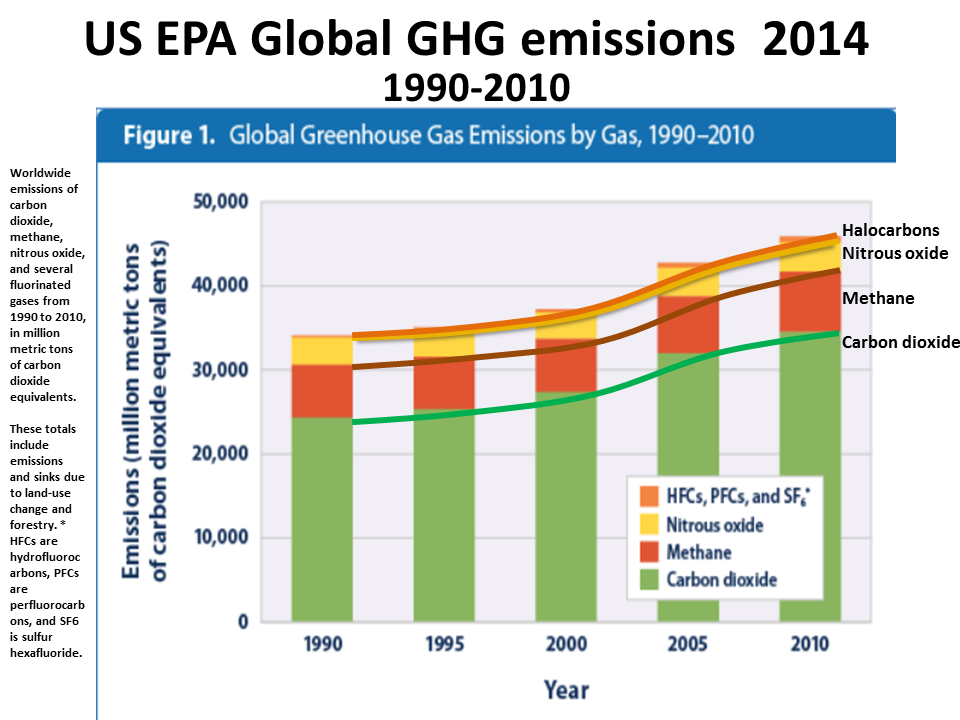
Atmospheric CO2 is accelerating, at a 15 million to 20 million year high and the rate is a 20 million year high.
Ocean acidification is at a 20 million year high and a 300 million high for the rate (see Jelle Bijma 2013)
Ocean acidification is at a 20 million year high and a 300 million high for the rate (see Jelle Bijma 2013)
Since 2000 concentrations of all three main GHGs are rising at an accelerating exponential rate. The post 2007 atmospheric methane increase is from feedback methane emissions.
The emergency is now recognized in the UN Paris Agreement . ' Recognizing that climate change represents an urgent and potentially irreversible threat to human societies and the planet
Also recognizing that deep reductions in global emissions will be required in order to achieve the ultimate objective of the Convention and emphasizing the need for urgency in addressing climate change'
Paris Agreement Dec 2015
However the 'Intended' national emissions targets puts the world on track for 3.5C up to 4.6C by 2100, which is 8C after 2100 (full equilibrium warming) from Climate Interactive. This is certain catastrophe to the entire human population and almost all life (judging by past mass extinction events). World food production would collapse by 2050.
SURVIVAL For the first time a July 2015 paper finds that our mismanagement of Nature puts our
survival in jeopardy
A NASA based 2014 computer model report warns of collapse of civilization
industrial civilisation headed for 'irreversible collapse'?
A 2015 climate food production projection finds that 'climate change
‘set to fuel global food crisis, (and this report also includes
bee pollinator colony death crisis due to pesticide use and climate change).
The definite global emergency today is because of today's committed global
climate change, with all climate change indicators accelerating (StateofOurClimate.com),and no agreement to reverse global emissions
(into decline)
Who does the emergency apply to?
As shown (click above link) the list has grown fast over the past decade.
Now it is almost all of us alive today, and certainly applies to all today's children everywhere and certainly
to all future generations
The fast changing Arctic is an emergency for the future of the life sustaining biospshere and life.
Also recognizing that deep reductions in global emissions will be required in order to achieve the ultimate objective of the Convention and emphasizing the need for urgency in addressing climate change'
Paris Agreement Dec 2015
However the 'Intended' national emissions targets puts the world on track for 3.5C up to 4.6C by 2100, which is 8C after 2100 (full equilibrium warming) from Climate Interactive. This is certain catastrophe to the entire human population and almost all life (judging by past mass extinction events). World food production would collapse by 2050.
SURVIVAL For the first time a July 2015 paper finds that our mismanagement of Nature puts our
survival in jeopardy
A NASA based 2014 computer model report warns of collapse of civilization
industrial civilisation headed for 'irreversible collapse'?
A 2015 climate food production projection finds that 'climate change
‘set to fuel global food crisis, (and this report also includes
bee pollinator colony death crisis due to pesticide use and climate change).
The definite global emergency today is because of today's committed global
climate change, with all climate change indicators accelerating (StateofOurClimate.com),and no agreement to reverse global emissions
(into decline)
Who does the emergency apply to?
As shown (click above link) the list has grown fast over the past decade.
Now it is almost all of us alive today, and certainly applies to all today's children everywhere and certainly
to all future generations
The fast changing Arctic is an emergency for the future of the life sustaining biospshere and life.
IPCC AR4 WG2 2007 chart of impacts - emergency for billions
All IPCC published impacts in one comprehensive impacts chart with temperature increases (2014 AGU presentation)
IPCC AR5 WG2 'Reasons for concern' dangerous impacts indicators
Arctic chart of observed impacts & committed global effects (2014 AGU presentation)
Arctic has switched from carbon sink to source NOAA Dec 2016 Arctic Report Card
Arctic has switched from carbon sink to source NOAA Dec 2016 Arctic Report Card
IPCC AR5 WG2 Increasing extreme weather events chart
Climate system commitment (inertia-momentum)
References by seperate chart
Commitment combined with impacts chart IEA WEO 2008 (the only such example)
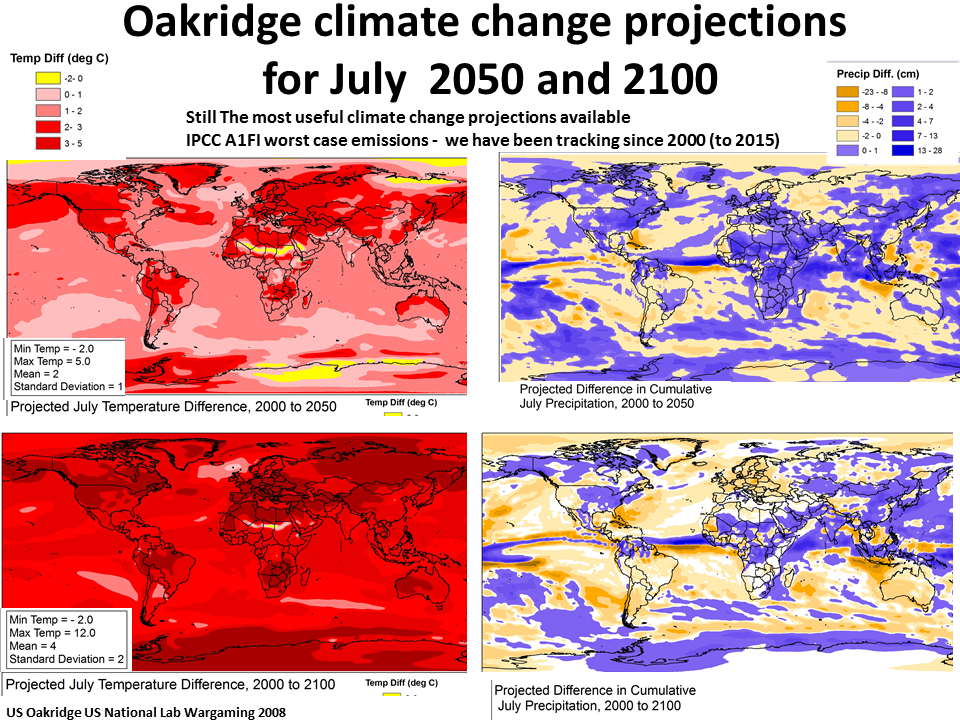
Already committed (locked in) global climate change.
1.5C by 2030-2040 and 2.0C by today's atmospheric GHGs. (IPCC AR5 WG1).
1.5C by 2030-2040 and 2.0C by today's atmospheric GHGs. (IPCC AR5 WG1).
IPCC 2014 AR5 Headline Statements 'Continued emission of greenhouse gases will cause further warming and long-lasting changes in all components of the climate system, increasing the likelihood of severe, pervasive and irreversible impacts for people and ecosystems'
o Mass extinctions implicate CO2 emissions, implicated the worst ever End Permian (2014 VIDEO),
when Earth nearly died.
when Earth nearly died.
J. Hansen 10 Sept 2015 his key quotes on the emergency
2019 UNEP Gap Emissions targets = 3.2C 2100
As reported in IPCC AR5 WG2 Food by a 2C warming all crop yields in all food producing regions will be in decline, except only for temperate rice.
Summer high temperatures will become too high for NH as well as tropical crops.
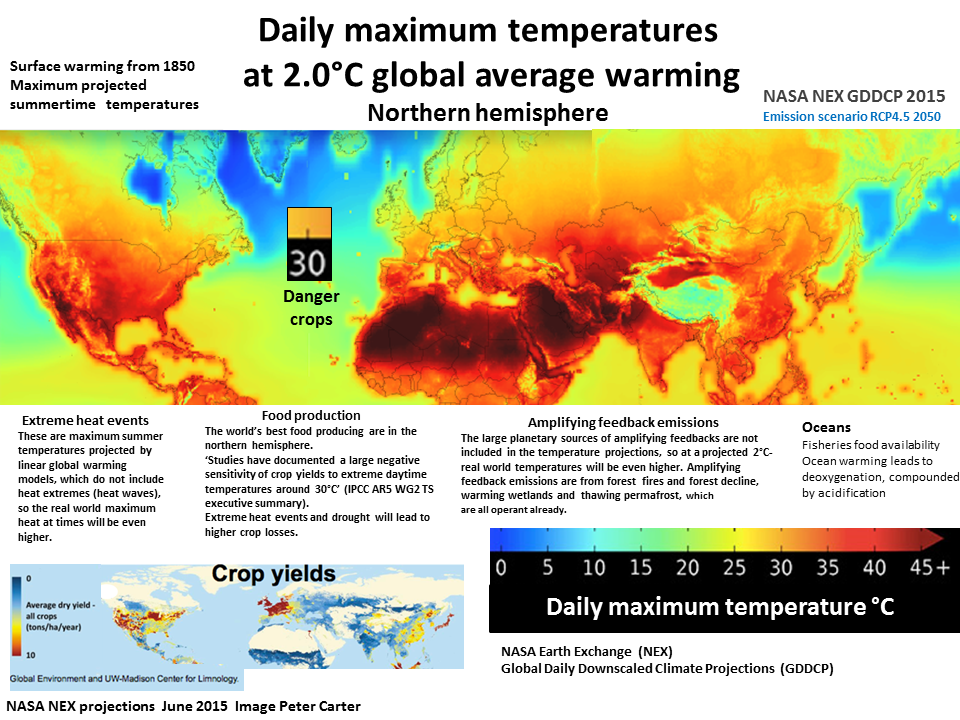
All indicators
are accelerating
Latest strongest evidence StateOfOurClimate.com
are accelerating
Latest strongest evidence StateOfOurClimate.com
14 Oct 2015 Uncertainty makes
action on climate change more urgent - not less
action on climate change more urgent - not less
o OCEANS Atmospheric CO2 & GHG pollution are causing rapid ocean warming (now going deep) acidification and deoxygenation- a catastrophic triple assault. Warming + acidification is projected to lead to irreversible collapse, which would be disastrous for live on land.
2012 DARA 400,000/year being killed by climate change
The most important IPCC finding ‘Projected future climate change and other human-induced pressures are virtually certain to be unprecedented compared with the past several hundred millennia’.
(AR4 WG2 Impacts 4.1 Key issues)
(AR4 WG2 Impacts 4.1 Key issues)
o From 2015 the global temperature increase is above 1.0C into the danger zone.
o The global temperature is increasing 100X faster than the natural end ice age war
ming and 10X faster the past 65 million years.
o The level of all main atmospheric GHGs are accelerating higher.
o In 2016 atmospheric CO2 and temperature rise were at a record and record increase in one year (boosted by El Nino) , even though industrial CO2 emissions (fossil fuel) did not increase in 2014 and 2015.
o Atmospheric CO2 is at a 3-5 million year high (possibly 15 million year high) and the CO2 rate of increase is unprecedented (WMO Oct 2017)
o Rate of industrial CO2 emissions is unprecedented in the past 65 million years , which 14,000 X faster than CO2 can be removed.
o The terrestrial biosphere is now a net source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere
o Tropical rainforests have switched from carbon sink to source
o The Arctic has switched from carbon sink to source
o Ocean acidification is at a 20 million year and 300 million increase rate high,
and accelerating.
o The global temperature is increasing 100X faster than the natural end ice age war
ming and 10X faster the past 65 million years.
o The level of all main atmospheric GHGs are accelerating higher.
o In 2016 atmospheric CO2 and temperature rise were at a record and record increase in one year (boosted by El Nino) , even though industrial CO2 emissions (fossil fuel) did not increase in 2014 and 2015.
o Atmospheric CO2 is at a 3-5 million year high (possibly 15 million year high) and the CO2 rate of increase is unprecedented (WMO Oct 2017)
o Rate of industrial CO2 emissions is unprecedented in the past 65 million years , which 14,000 X faster than CO2 can be removed.
o The terrestrial biosphere is now a net source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere
o Tropical rainforests have switched from carbon sink to source
o The Arctic has switched from carbon sink to source
o Ocean acidification is at a 20 million year and 300 million increase rate high,
and accelerating.
"It (record of 2015 -16) emphasises that we have no carbon budget left for the 1.5°C target and the opportunity for holding to 2°C is rapidly fading unless the world starts
cutting emissions hard right now". Prof M. Mann Mar 2016
2015 Paris Agreement 16% more global emissions in 2030 than today. May 2016 update no change
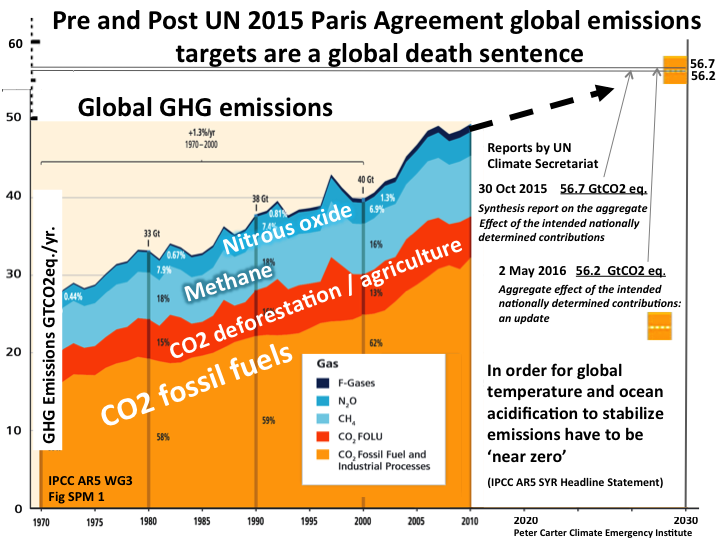
UFCCC 2011 To avoid going over 2-2.4C global
emissions had to be in decline from 2015
emissions had to be in decline from 2015
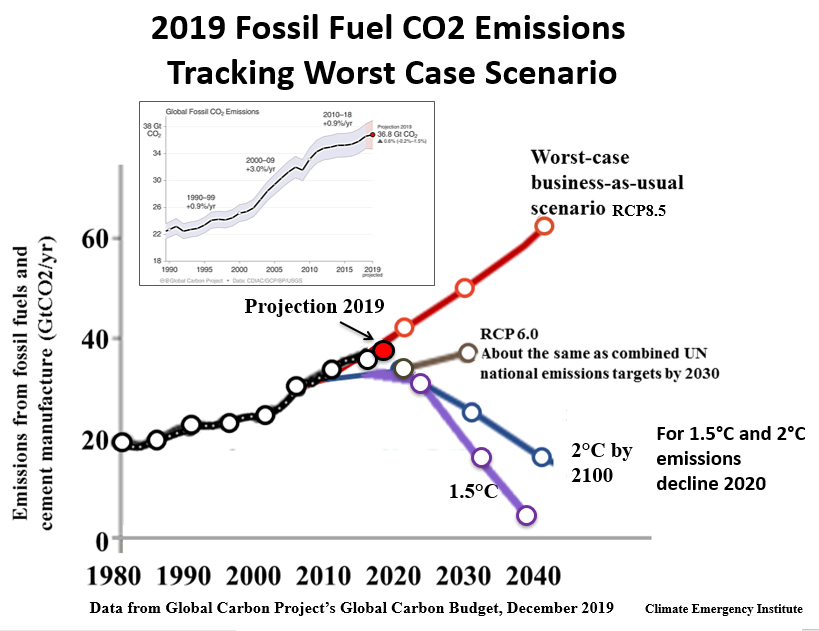
2019 global CO2 emissions
on worst case scenario
(Global Carbon Project Dec 2019)
on worst case scenario
(Global Carbon Project Dec 2019)
WMO GHG Bulletin 2017 Atmos CO2 increase rate unprecedented
Sept 2017 Amazon switch carbon sink to source
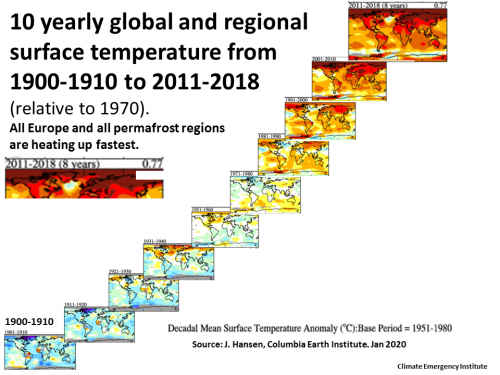
27 Nov 2019 Climate tipping
points — too risky MUST ACT NOW
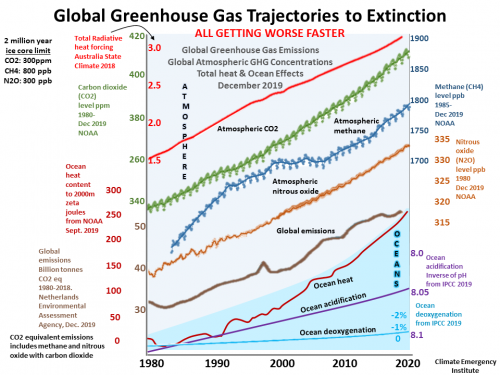
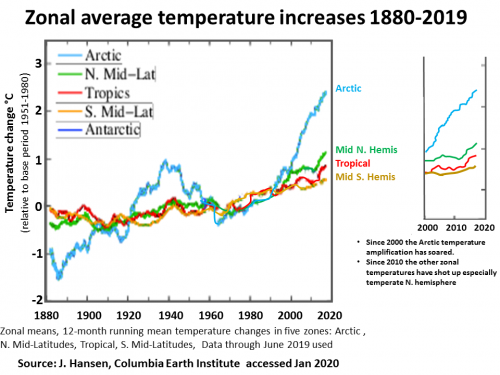
Emergency evidence in IMAGES