Runaway
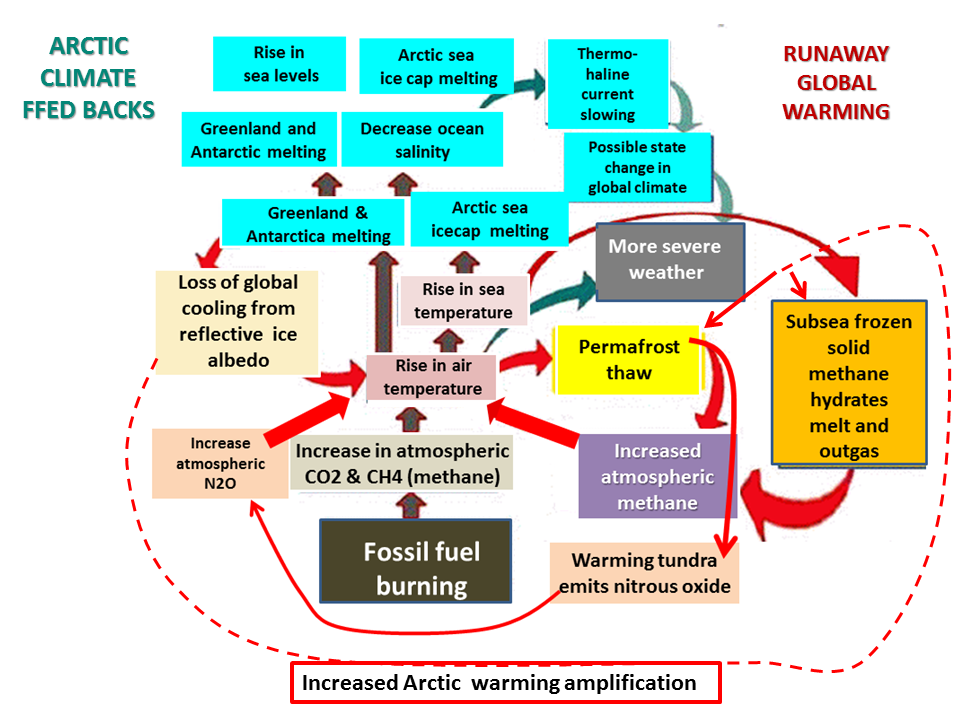
Each one of these is a powerful positive feedback in increasing the rate of global warming, as well as of course Arctic warming.
Because they all occur in the same region of the Arctic, they will each reinforce all the others, a domino effect called cascading feedbacks.
The Arctic warms more rapidly than the rest of the planet. (Arctic polar amplification).
The Arctic summer sea ice is collapsing past its tipping since 2007.
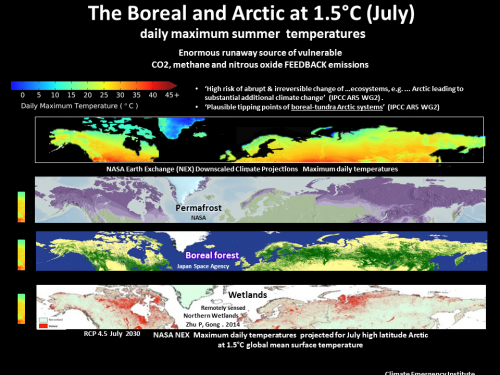
The rapidly warming Arctic is already emitting methane from all the above sources. As global warming is committed to increase and Arctic warming increases faster, we are now in a runaway planetary emergency situation.
CLIMATE EMERGENCY INSTITUTE
The Health and Human Rights Approach to Climate Change
The danger hs been known for years
Feb 2017 dynamics of runaway global warming explained (2017 B. Parker page 15)
IPCC 3rd assessment on runaway IPCC TAR 2001 Ch 19 19.6.3.2. Large-Scale Singularities Runaway carbon dynamic. ). These (Arctic) changes will have cascading effects on key regional bio-physical systems and cause global climatic feedbacks (IPCC 2001 Ch. 15
IPCC 2007 4th assessment Arctic Surface albedo is projected to decrease ... higher methane emissions responding to the thawing of permafrost and an overall increase in wetlands will enhance radiative forcing (AR4 2007 WGII Chapter 15: Polar Regions)
This is a good definition of runaway from a 2018 paper
Self-reinforcing feedbacks could push the Earth System toward a planetary threshold that, if crossed, could prevent stabilization of the climate at intermediate temperature rises and cause continued warming on a “Hothouse Earth” pathway even as human emissions are reduced.
This paper warns that 'warming could activate important tipping elements (12, 17), raising the temperature further to activate other tipping elements in a domino-like cascade that could take the Earth System to even higher temperatures (Tipping Cascades)'. Even if the Paris Accord target of a 1.5 °C to 2.0 °C rise in temperature is met, we cannot exclude the risk that a cascade of feedbacks could push the Earth System irreversibly onto a “Hothouse Earth” pathway.' As we are committed to 2C without immediate rapid global emissions decline we are now at a point of runaway extreme risk.
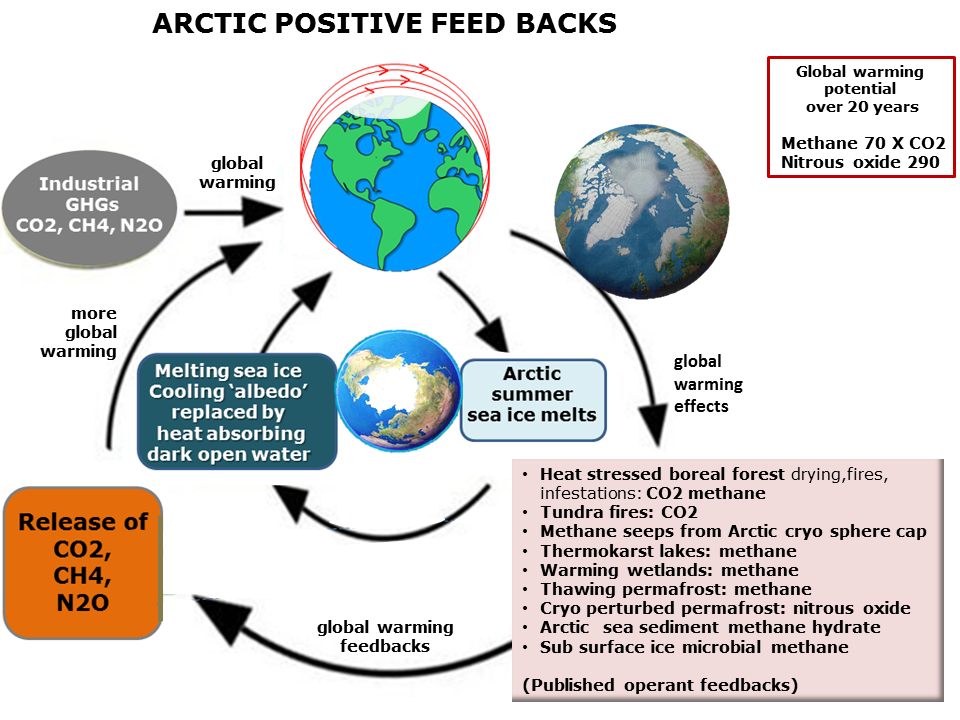
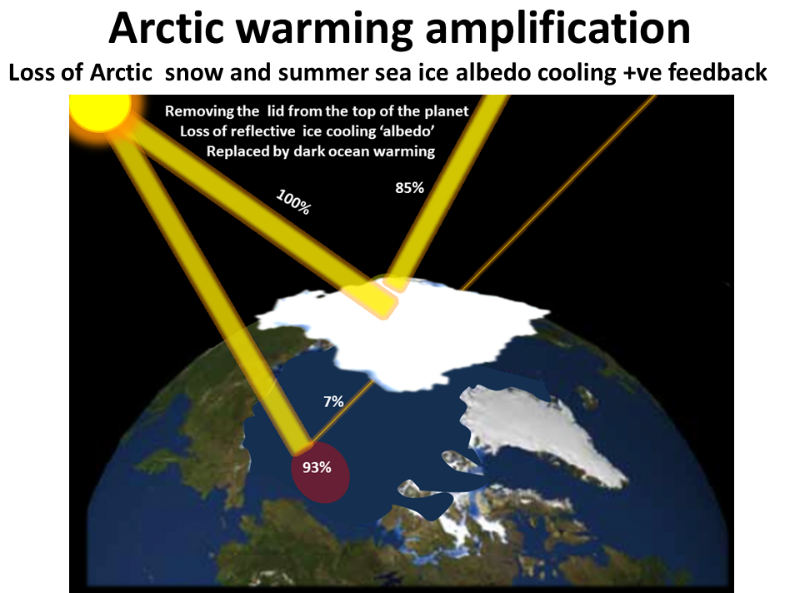
This NOT the 'runaway greenhouse effect" dead planet like Venus. Runaway is worst End the world climate change scenario, and not a popular thing to investigate. It based on high degrees of committed future warming, that have the future potential to cause increasing emissions from large (previously) quiescent pools of carbon. It is GHGas runaway- multiple self and inter-reinforcing GHG emissions that have been safely balanced (carbon cycle) cold (subarctic wetlands) or frozen solid(Arctic frozen soil permafrost). Arctic warming from global warming is self amplifying due to melting summer sea ice losing ice 'albedo' cooling effect.
UN Sec. General Sept. 2018 If we do not change course by 2020, we risk missing the point where we can avoid runaway climate change. Though the IPCC reports multiple Arctic feedback sources it does not recognize runaway
MORE THAN ASSUMED
'Runaway climate change' here is the result of the known multiple self and inter-reinforcing amplifying feed-backs caused by global warming beyond the control of mitigation and cannot be adapted to. It is NOT the end of all life 'runaway greenhouse effect', a science term (2012 paper). A recent paper addresses multiple feedbacks and tipping points acting in concert to a different Hothouse Earth state, which would be runaway.
2018 Hothouse runaway Earth paper: 2C trigger MOST IMPORTANT PAPER
Dec 2019 Charles Rhodes on Thermal Runaway
VIDEO On 25 June 2020 the UN Climate Secretariat put out a warning on Twitter "To avoid run-away climate change we act now".
Runaway climate change is rarely mentioned by climate change assessments. Several large sources of feedback emissions are recognized,and also tipping points. The combined effect of multiple feedbacks or tipping points acting in concert is not addressed. The scientists use the term 'beyond the point of no return', but this is not in the assessments.
The only 'runaway' generally used in the science is the runaway greenhouse effect which results in a dead planet and applies to Venus.
The situation of 'runaway' climate change in the science is 'runaway carbon dynamics' and this is only to be found in the IPCC 2001 3rd assessment under 'large scale singularities' (above). It is not included in the 2014 IPCC 5th assessment. Runaway carbon dynamics means amplifying carbon feedbacks of CO2 and methane from the heated up planet, or weakening of the land or ocean carbon sinks. However feedback emissions of nitrous oxide are also caused by global warming, so the more complete term would be runaway GHG dynamics.
Long ago an Oct 2005 presentation (at Yale) by the IPCC Chair R Pachauri included 'runaway carbon dynamics' in a list of singular events
'Instances of possible singular events
• Breakdown of the thermohaline circulation
• Disintegration of the West Antarctic ice sheet
• Shift in mean climate towards an El Nino like state
• Runaway carbon dynamics - reduced sink capacity, release of methane from hydrates, carbon from permafrost
• Rearrangement of biome distribution
Such events can overwhelm our response strategies'
From the very start the big concern about global warming has been the possibility of a 'runaway' global warming and climate change.
'Runaway' (self accelerating) global heating and climate change is the planetary tipping point of many tipping points combined and in the case of the many Arctic amplification tipping points are self and inter reinforcing. Ultimate vicious cycles.
This is the greatest single danger from global warming to the survival of humanity and also the survival of potentially almost all life on the planet. With all climate and ocean indicators accelerating (2016) humanity and life are in extreme peril from runaway.
A global heating feedback event wiping almost most life we know is possible- because it happened 250 million years ago in the End Permian extinction event and 55 million years ago with the Paleocene-Eocene thermal maximum (PETM). Current research confirms both of these extinction events were driven by very large emissions of carbon to the atmosphere.
The PETM is the closest distant past analog to our GHG emissions global warming situation today. Research published October 2013 by Morgan Schaller and James Wright leads to their definite finding that following a doubling in carbon dioxide levels, the surface of the ocean turned acidic over a period of weeks or months and global temperatures rose by 5 degrees centigrade – all in the space of about 13 years. Scientists had previously thought this process happened over 10,000 years.
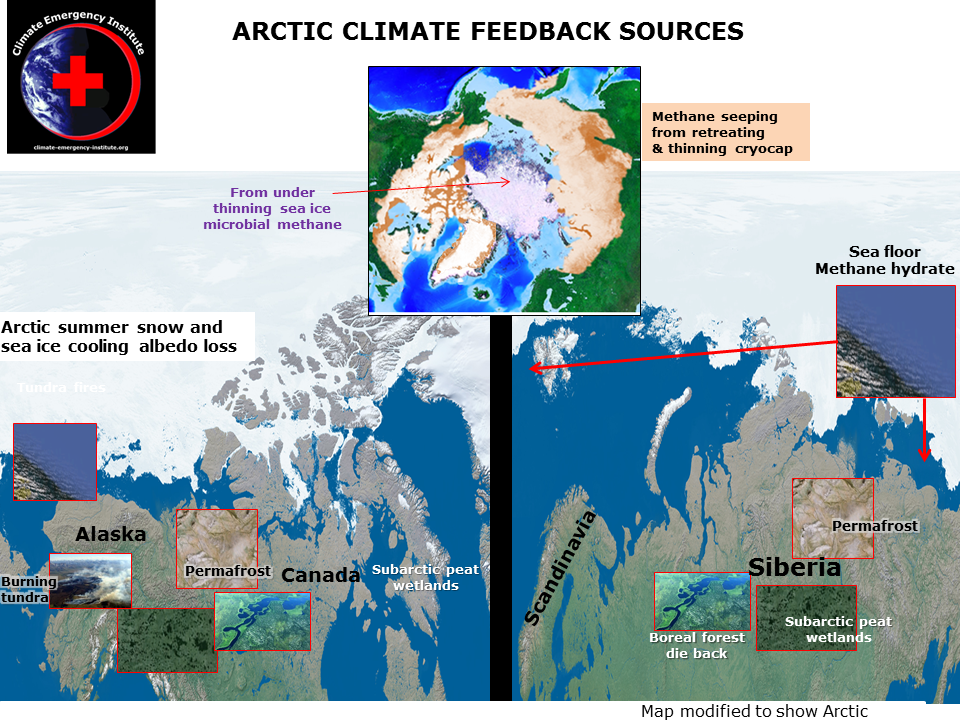
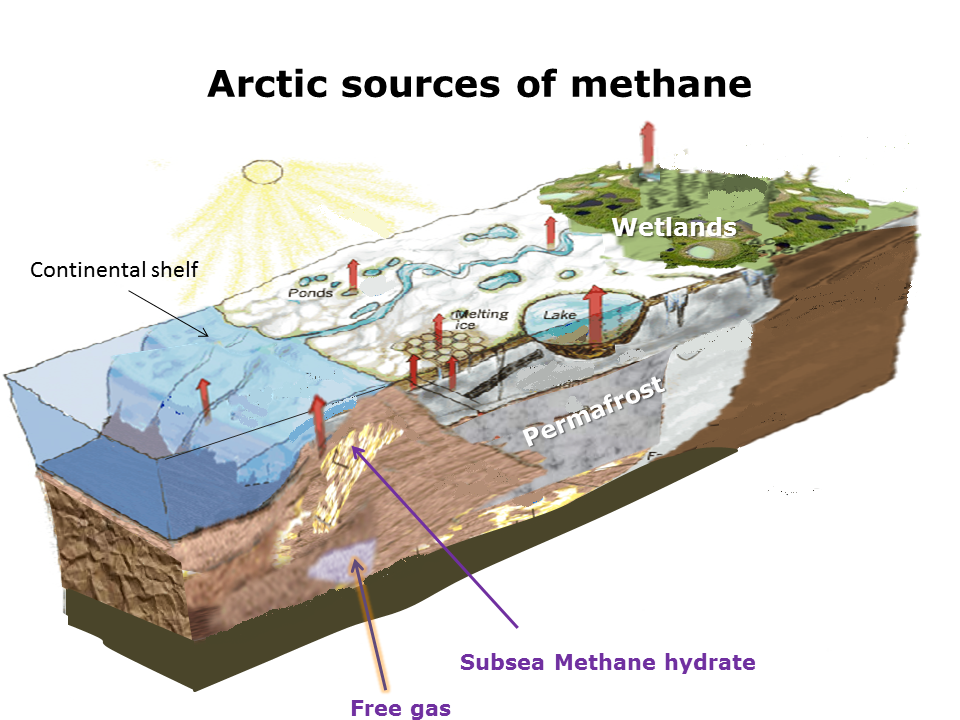
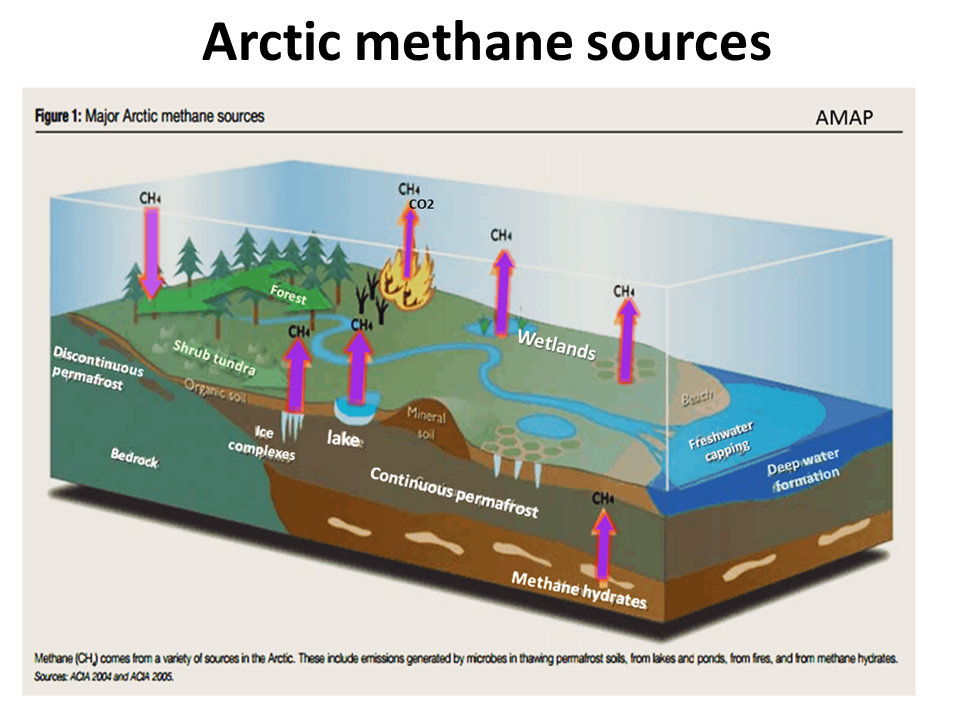
These mass extinction events involve the emission of an enormous emission of carbon as CO2 and methane. In the Arctic several times atmospheric methane is stored frozen in permafrost and subsea floor frozen solid methane gas hydrate. The permafrost is thawing as the Arctic temperature rapidly increases (Arctic amplification). Arctic methane hydrate is destabilizing in at least three locations, mainly a process that has been going on for a long time, but that ocean warming will make worse.
It is or should be treated as a zero tolerance risk applied to the very long time frame into the future.
Right now we are in a very high risk of committed runaway situation, meaning we are committing ourselves and all life to a rapid accelerating global heating that we could not possibly change. James Hansen has been warming about this for many years.
Runaway results from the combination of multiple triggered amplifying large feedbacks and climate change commitment.
Runaway includes methane feedback emissions- especially the enormous stores of Arctic carbon as methane emitters. Carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide feedback GHG sources are also huge. In runaway all three would be self reinforcing and accelerating.
Methane has a global warming effect of 86X CO2 for 20 years after emissions
Atmospheric methane having increased two and a half times since industrialization stalled in 2000 but from 2006 a renewed sustained increase started - and the scientists attributed this increase to planetary methane feedback emissions. The methane they think is coming from warming tropical and subartic wetland peat.
It seems most of the methane was being emitted from warming tropical wetland but the largest increase is from Far North wetland peat.
The highest atmospheric methane on the planet is recorded at Lac La Biche Alberta right on the southern edge of Canada's vast wetlands.
Tipping points, irreversible impacts, and singularities are scientific terms that apply.
James Hansen says
Runaway greenhouse effect" has several meanings ranging from, at the low end, global warming sufficient to induce out-of-control amplifying feedbacks such as ice sheet disintegration and melting of methane hydrates, to, at the high end, a Venus-like hothouse with crustal carbon baked into the atmosphere and surface temperature of several hundred degrees. Between these extremes is the "moist greenhouse", which occurs if the climate forcing is large enough to make H2O a major atmospheric constituent (Kasting, 1988). In principle, an extreme moist greenhouse might cause an instability with water vapor preventing radiation to space of all absorbed solar energy, resulting in very high surface temperature and evaporation of the ocean (Ingersoll, 1969). Our simulations indicate that no plausible human-made greenhouse gas forcing can cause an instability and runaway greenhouse effect as defined by Ingersoll (1969), Sept 2001 Climate Sensitivity, Sea Level, and Atmospheric CO2.
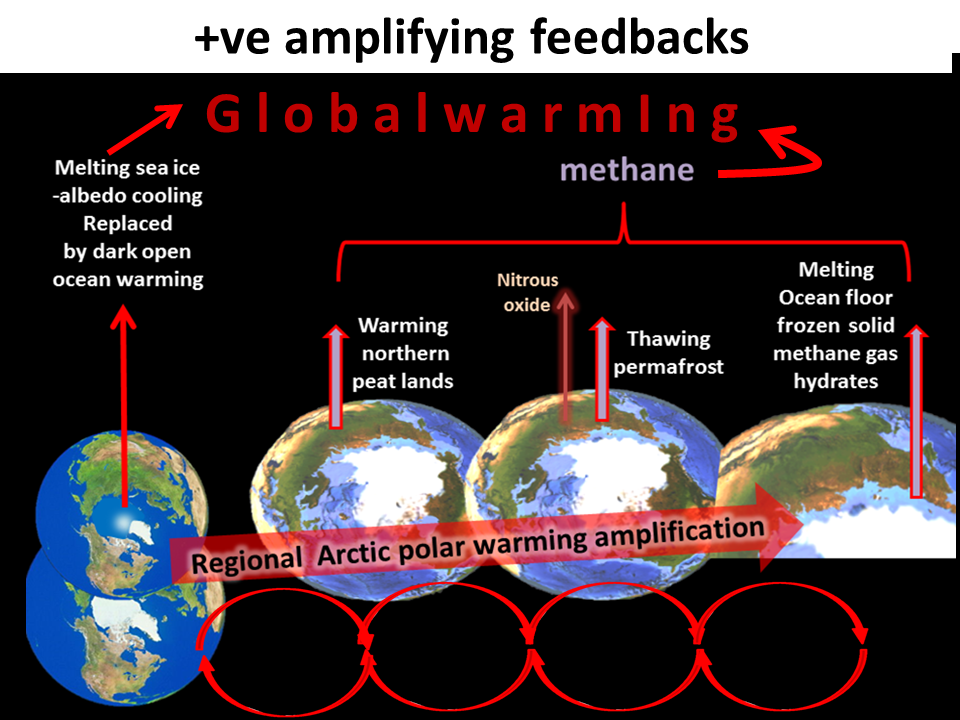
The runaway Arctic +ve feedbacks
Loss of Arctic snow and summer sea ice cooling albedo
Methane emissions from warming sub Arctic peat rich wetlands
Methane and carbon dioxide emissions and from thawing permafrost
Nitrous oxide emissions from thawing permafrost
Methane emissions from sub sea floor frozen solid methane gas hydrate