The Arctic
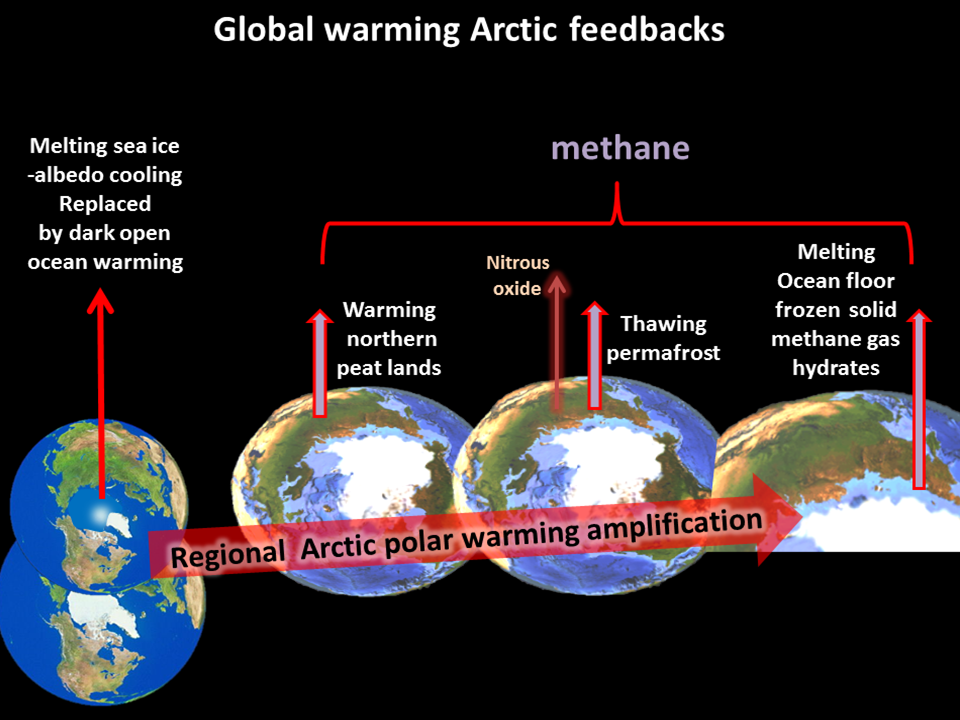
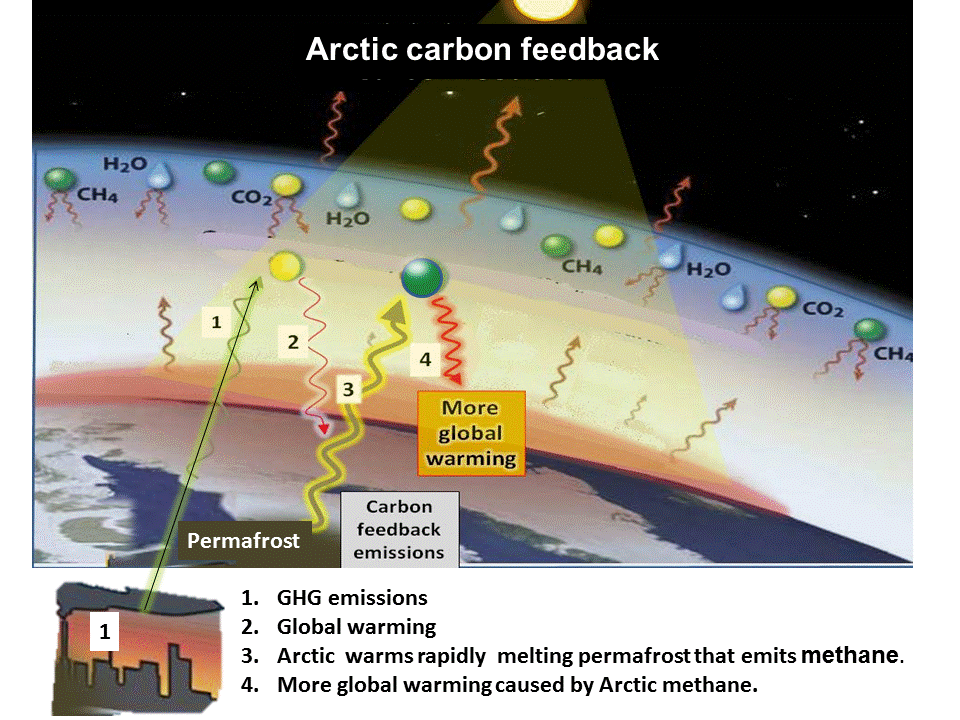
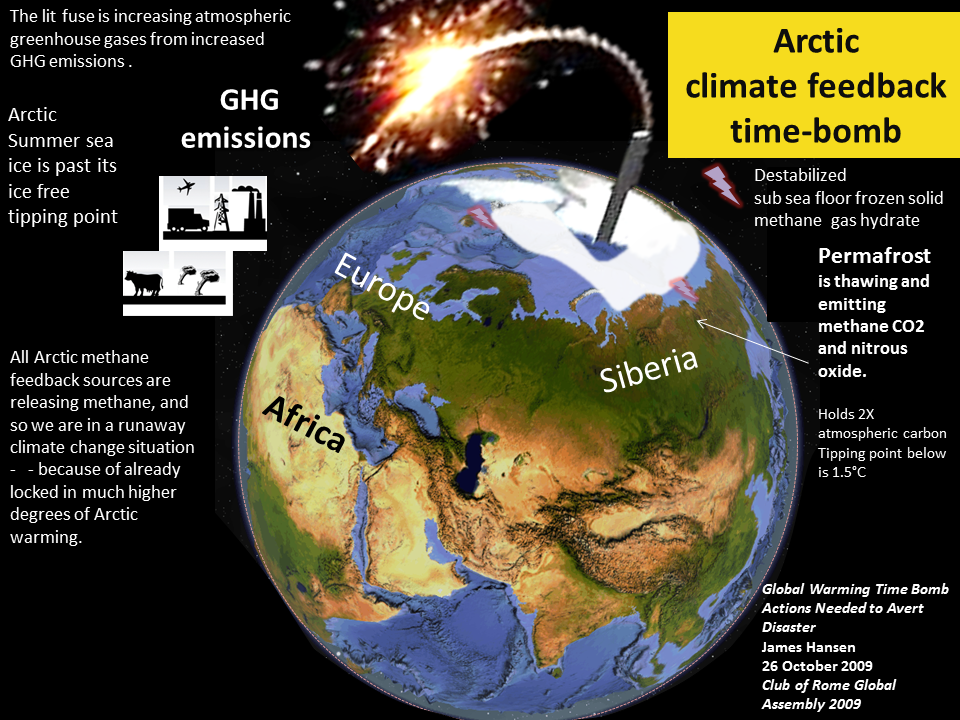
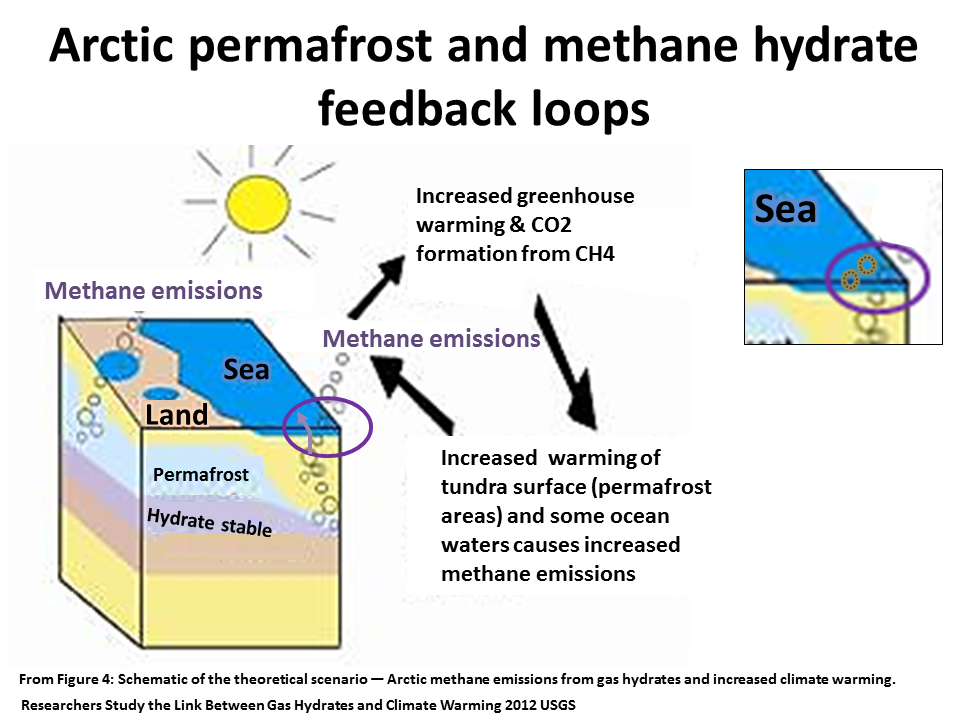
The sources of methane feedback emissions are warming wetlands, thawing permafrost and warmed sea floor methane hydrates.
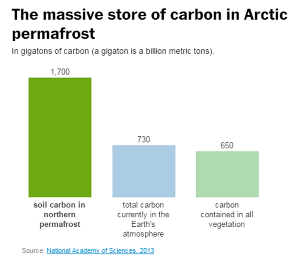
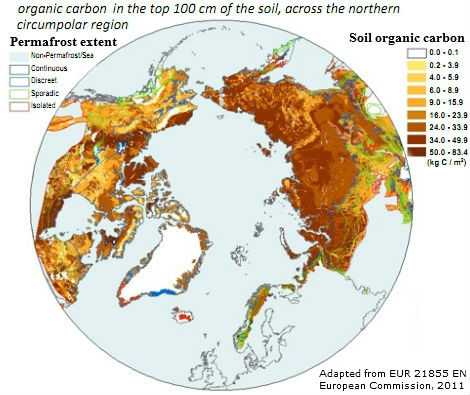
These regions hold three to four times all the carbon in the atmosphere.
The loss of all the summer sea ice will increase the rate of Arctic warming 3.5 times (D Lawrence 2008) which will boost the rate of methane emissions from the Arctic.
Since the record sea ice loss of 2007, the atmospheric methane concentration has been increasing and the scientists say this increase is due to carbon feedback emissions, some of which are coming from the rapidly warming Arctic.
Wetlands and methane hydrate can both respond rapidly to an increase in global warming. Arctic Methane hydrate has the potential to abruptly release a catastrophic amount of methane to the atmosphere.
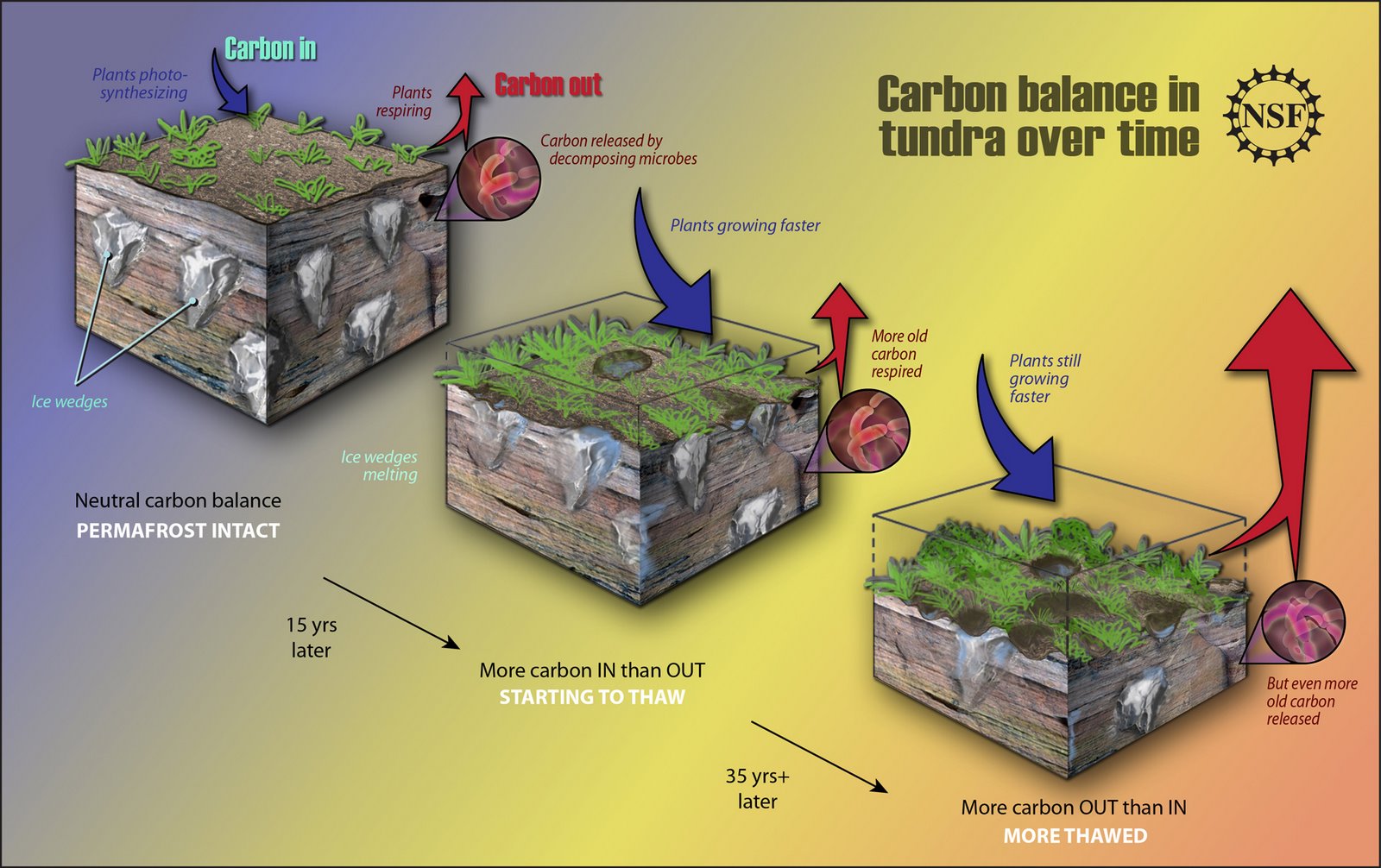
Land based permafrost responds slower to warming as the methane is emitted as a result of micro-organisms digesting the thawed organic material.
However at a certain amount of thawing permafrost thaw becomes self perpetuating - irreversible. This because the microbial activity generates heat indide the thawing permafrost.
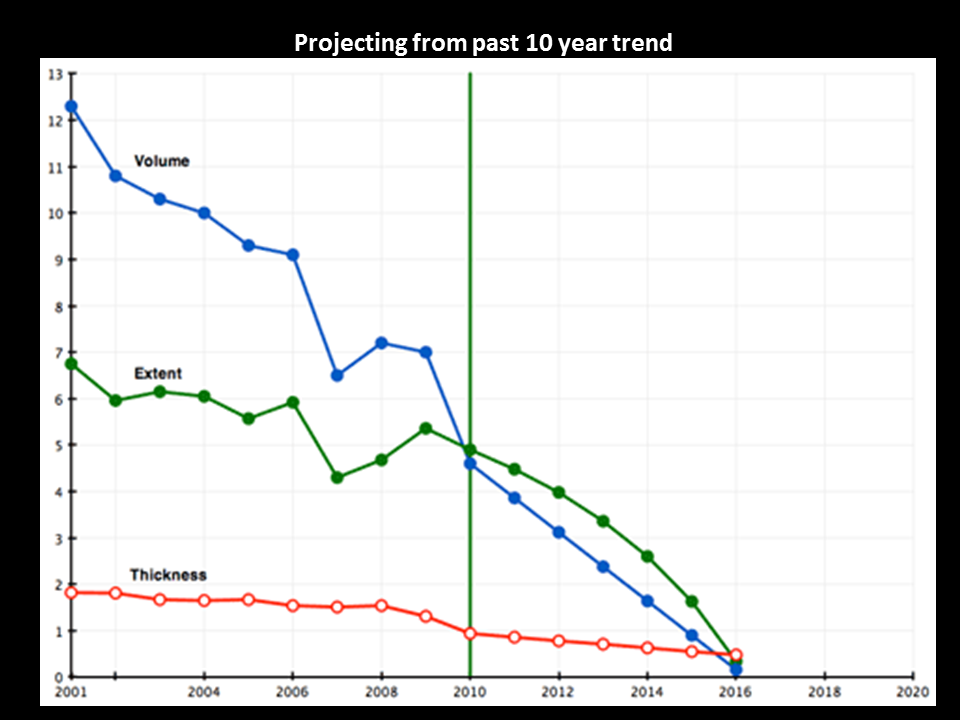
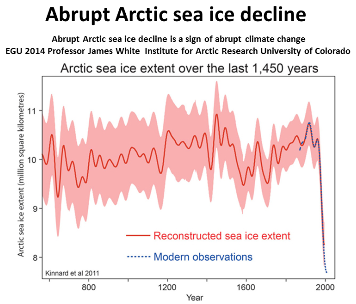
Arctic sea ice past ice free tipping point.
The first great Arctic amplifying feedback domino is falling and others are starting.
James Hansen made public statements in 2008 and in 2012 following the two record drops in Arctic Summer sea ice- warning the world had entered a state of planetary emergency. The reason is that, as he said in 2008, the Arctic sea ice had crossed its ice free tipping point in 2007, which is a very large +ve amplifying feedback. This will boost Arctic feedback GHG emissions and the rate of the Greenland ice sheet melt, both being planetary catastrophes. Tipping point expert Tim Lenton has also said he thinks the Arctic summer sea ice is past tipping the point.
Two Arctic methane science papers prove we have an Arctic warming planetary emergency. In 2013 A Vask's research of Siberian Permafrost caves determined that the vast Siberian permafrost has a tipping point for thawing of only 1.5C and that global climates only slightly warmer than today are sufficient to thaw extensive regions of permafrost. We are absolutely committed to a 1.5 warming due to the ocean heat lag alone.
202 record slide presentation
Research papers By date
20 May 2025, Warming of +1.5 °C is too high for polar ice sheets, C.R. Stokes et al
12 Jan. 2025. Wildfires offset the increasing but spatially heterogeneous Arctic–boreal CO2 uptake
14 Oct. 2024, Vulnerability of Arctic-Boreal methane emissions to climate change
2022, Carbon Cycle Feedbacks from A Warming Arctic, E. Schurr et al
26 Feb 2021 New Study Advances the Science of Arctic Climate “Warning” (1.3X atmosphere)
8 Feb 2021 (Methane blow-out crater) New Catastrophic Gas Blowout and Giant Crater on the Yamal Peninsula in 2020: Results of the Expedition and Data Processing
8 Jan 2021 Anomalous collapses of Nares Strait ice arches leads to enhanced export of Arctic sea ice
22 Dec 2020 Subsea permafrost carbon stocks and climate change sensitivity estimated by expert assessment. Release significant carbon by 2050
(60 billion tones methane
560 billion tons organic carbon)
10 Dec. 2020 Iron mineral dissolution releases iron and associated organic carbon during permafrost thaw More CO2 released- not lees by iron binding
12 Nov 2020 An earth system model shows self-sustained melting of permafrost even if
all human GHG emissions stop in 2020 RUNAWAY is triggered
21 Oct 2020 Large loss of CO2 in winter observed across the northern permafrost region (Arctic C switched to carbon source)
16 Oct 2020 "Arctic warming by only a few degrees may suffice to abruptly activate large-scale permafrost thawing" Remobilization of dormant carbon from Siberian-Arctic permafrost during three past warming events, Martens et al. 27,000 yrs
9 Oct 2020 East Siberian Sea Is Boiling With Methane (localised but IT DOES VENT) VIDEO
24 Oct 2020 Antarctic melting Strong ice-ocean interaction beneath Shirase Glacier Tongue in East Antarctica
14 Sept 2020 Extremes become routine in an emerging new Arctic
25 Aug 2020 Large stocks of peatland carbon and nitrogen are vulnerable to permafrost thaw
August 13 2020 Warming Greenland ice sheet passes point of no return -melt
10 Aug 2020 New study warns: We have underestimated the pace at which the Arctic is melting- it's abrupt & may lead to abrupt global heating
March 2020 East Siberian Arctic inland waters emit
mostly contemporary carbon
21 Feb 2020 Old Carbon small last deglaciation
4 Feb 2020 Permafrost collapse is speeding climate change 3 Feb 2020 Abrupt permafrost paper
10 Jan 2020 Ice-free Arctic Ocean allowed ancient carbon leaks
June 2020 Arctic Amplification of Global Warming Strengthened by Sunlight Oxidation of Permafrost Carbon to CO2
Models underestimate 14% from this process
8 Jan 2020 Palaeoclimate evidence of vulnerable permafrost during times of low sea ice, A Vaks
Dec 2019 NOAA Arctic Report Card Arctic switched from C sink to source confirmed. Permafrost feedback underway
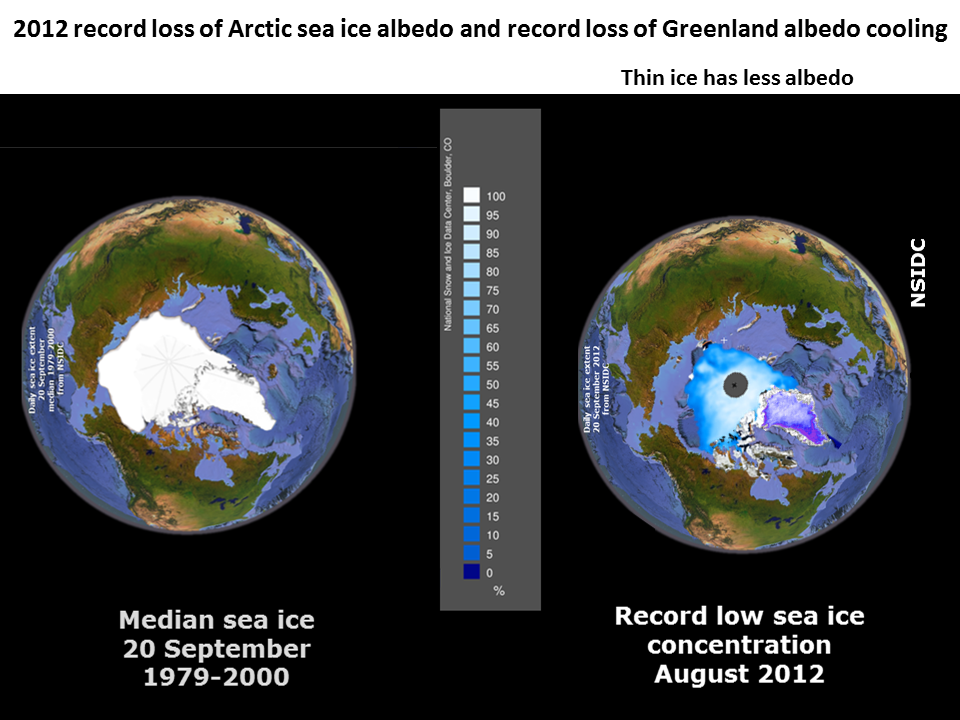
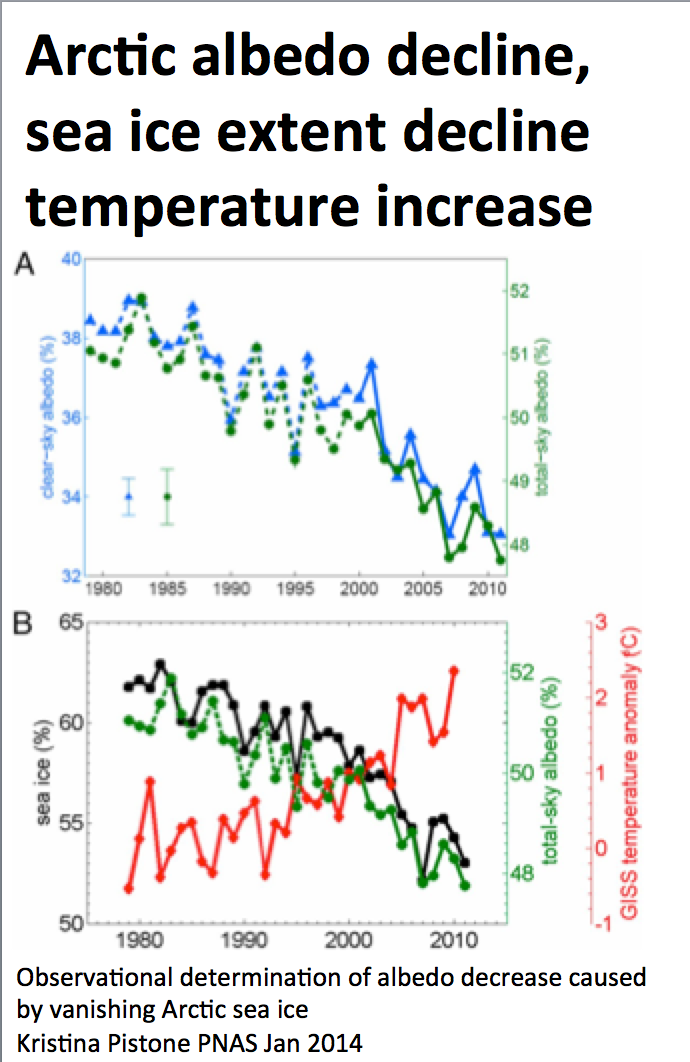
11 Nov 2019 Unraveling driving forces explaining significant reduction in satellite-inferred Arctic surface albedo since the 1980s (-1.15 to 1.51%/decade)
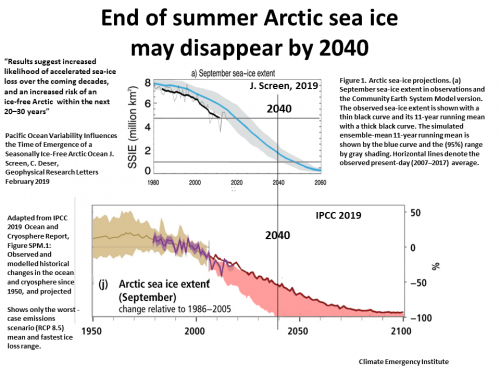
11 Nov 2019 Chad Thakeray Arctic could be ice free by 2044
Arctic net Carbon source
Large loss of CO2 in winter observed across the northern permafrost region
11 Sept 2019 Western Siberian rivers and lakes emit greenhouse gases into the atmosphere
16 July 2019 ANTARCTIC 40-year record Antarctic sea ice increases followed by decreases at rates far exceeding the rates seen in the Arctic
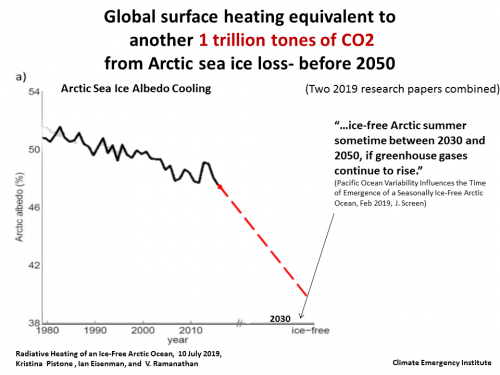
10 July 2019 Radiative heating of an ice free Arctic ocean +i trillion tons CO2
A novel method to test non-exclusive hypotheses applied to Arctic ice projections from dependent models Sept sea-ice free 1.5C-2C
8 July 2019 Responses of tundra soil microbial communities (permafrost thaw)
1 July 2019 Direct observation of permafrost degradation and rapid soil carbon loss in tundra (5/year!)
10 June 2019 Maximum permafrost thaw depths already exceeding those projected for 2090 Climate change drives widespread and rapid thermokarst development in very cold permafrost in the Canadian High Arctic.
17 May 2019 United States Heat Wave Frequency and Arctic Ocean Sea Ice (Gt Plains)
30 April 2019 Permafrost collapse is accelerating carbon release
23 April 2019 Climate policy implications of nonlinear decline of Arctic land permafrost
15 Jan 2019 Rapid decline of Arctic sea ice volume: Causes and consequences (2030-2035)
March 2019 UN Arctic Global Linkages
5 Feb 2019 Sea Ice free by 2035 Pacific Ocean Variability Influences the Time of Emergence of Ice‐Free Arctic Ocean (by 2040)
5 Dec 2018 Declining sea ice is making the Arctic ocean warmer (Fall and early Winter)
Oct 2018 Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: losses (1958–2018) -66% in 50 yrs (Kwok)
Sea level rise in the past led to the release of greenhouse gases from permafrost
15 Aug. 2018 21st-century modeled permafrost carbon emissions accelerated by abrupt thaw beneath lakes Abrupt thaw beneath thermokarst lakes will more than double radiative forcing from polar permafrost-soil carbon fluxes this century.
2018 Deglacial mobilization of pre-aged (ancient) terrestrial carbon from degrading permafrost permafrost-carbon release through sea-level rise likely contributed significantly to abrupt increases in atmospheric CO2 around 14.6 and 11.5 kyrs BP
6 Mar 2019 Sea ice -abrupt climate change
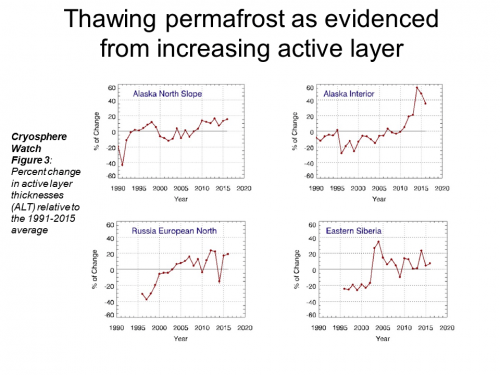
16 Jan 2019 Permafrost is warming at a global scale (rapid-Arctic continuous accelerating)
2012. Significant contribution to climate warming from the permafrost carbon feedback, Macdougall et al
to 2014
While the most talked about Arctic global catastrophe is sea level rise from the meltdown of the Greenland ice sheet, that is the last of our Arctic worries.
Before that is abrupt climate change from the slowing of the deep ocean conveyor current (MOC) from the fresh melt-water, which is slowing faster than expected (research March 2015). The worst case MOC scenario 'Imagining the Unthinkable' was published in 2003.
Long before that happens there is the effect on the Northern Hemisphere (NOAA refs), which includes the world's best agriculture
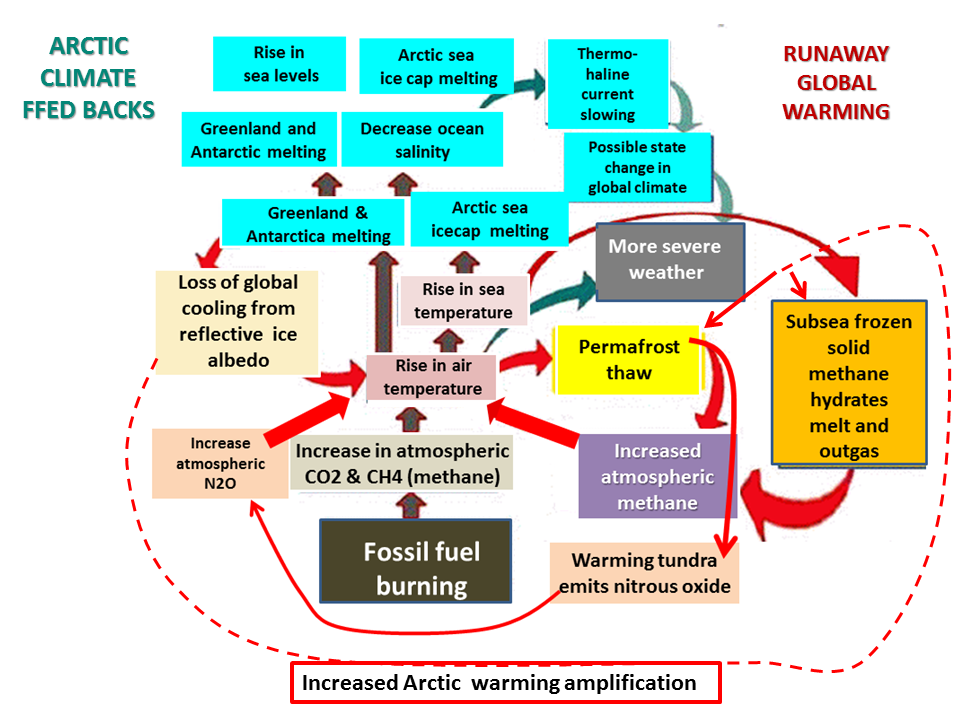
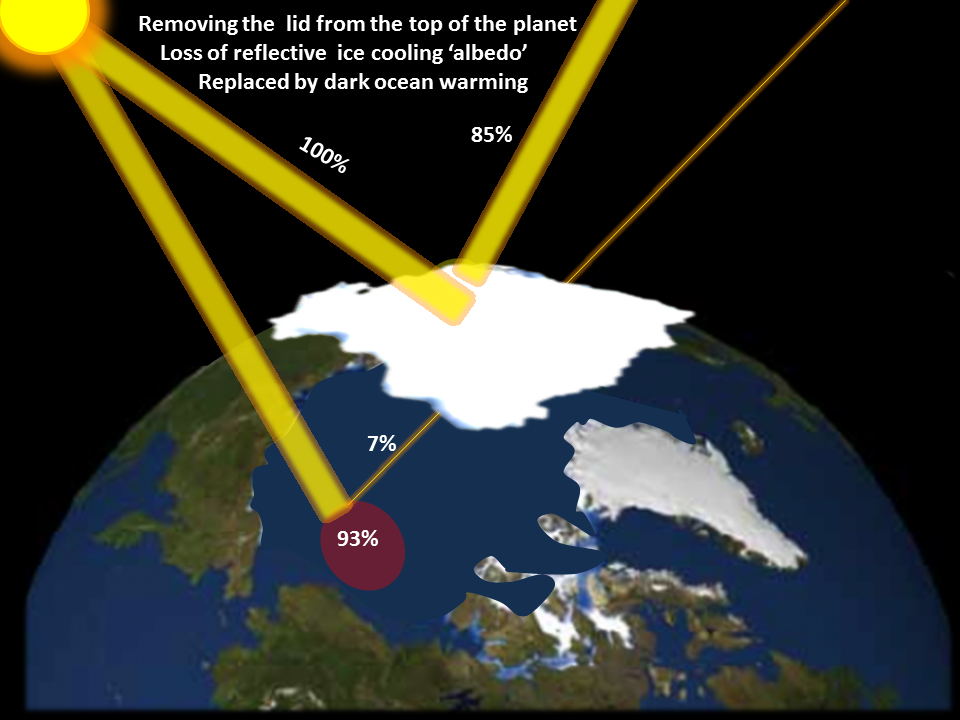
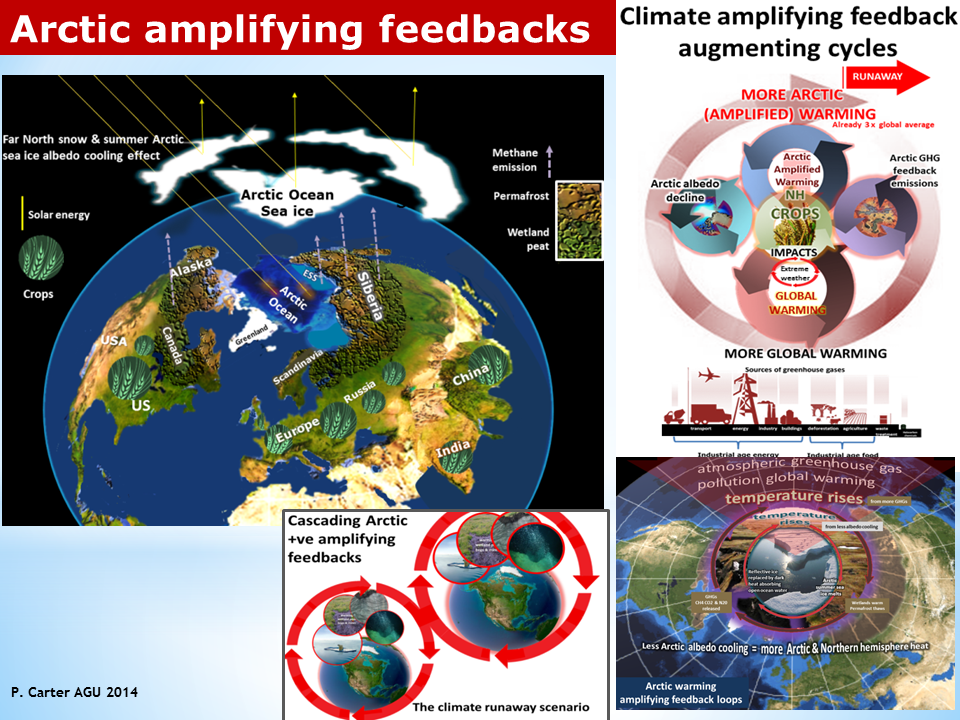
Worst of all is Arctic multiple amplifying feedback 'runaway', which starts with the snow & ice albedo amplifying feedback.
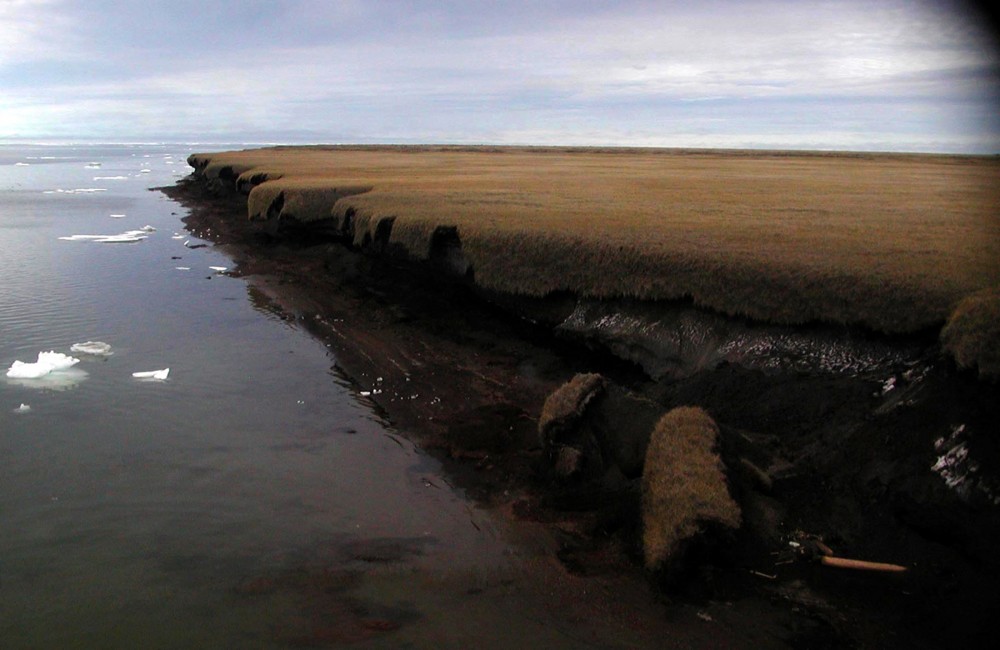
Arctic permafrost is vast & deep
TEDEd Why the Arctic is climate change's canary in the coal mine - William Chapman (animation)
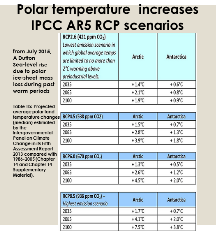
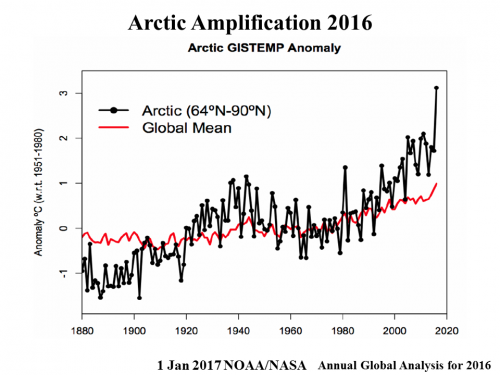
The Arctic is warming up to 4X the global average
Arctic permafrost carbon 350 PgC by 2100+1.5C by 2100 (IPCC AR5 WG1 FAQ 6.1)
Multiple amplifying
Arctic feedbacks
Arctic amplification
PERMAFROST 26 Oct 2015 Ancient (yedoma) permafrost quickly transforms to carbon dioxide upon thaw, contrary to assumptions. 2008 field research found permafrost holds double the carbon of assumed estimates, which is double atmospheric carbon.
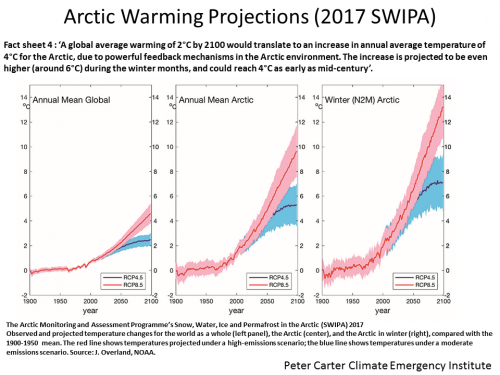
April 2017 Between 1976 and 1996 average sea ice loss in the Arctic was 8,300 square miles per year. Between 1996 and 2013, this number more than doubled to 19,500 square miles per year. April 2017 AMAP SWIPA SPM (AMAP: Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme). NOAA 2018 95% of thick old ice lost
At 2.2C global warming, daily maximum temperatures are above zero C for all regions of Arctic permafrost
Earth Emergency Arctic has switched from carbon sink to source with accelerating
permafrost feedback underway NOAA Arctic Report Card 2019
March 2019 Sea ice role in abrupt climate change
(Winter)
The Arctic Carbon Time-Bomb is Triggered 2019 PDF
2017 Strong Methane emissions from Canada Arctic permafrost
July 2019 Total Arctic sea ice loss = 1 trillion tons CO2 emissions/25 years global warming
NASA sea ice age/thickness visualization 1984-2019
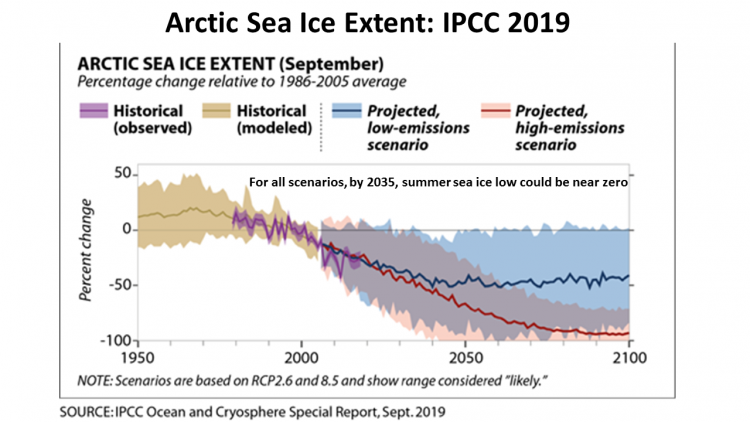
Sept 2019 IPCC Cryosphere (snow/ice) Report Cryosphere extracts
VIDEO Oct 2019 Carbon emissions grow exponentially, Arctic permafrost thaws faster
17 July 2019 Arctic temperature hits huge record 21°C
12 Nov 2020 Earth Emergency Arctic feedback RUNAWAY triggered
Site maintained by Peter Carter